1. Introduction: PCR amplifies DNA
Here’s something you’ll see in almost any police or detective drama. There’s a crime. Whoever committed the crime escaped unseen. Detectives arrive and search the crime scene for traces of hair or skin that might belong to the criminal. The samples go into a tiny zip loc bag that they take back to their lab so that they can look for DNA evidence to link the criminal to the crime.
The next step often doesn’t make it into the show. A technician has to take that tiny trace of DNA and make enough DNA so that it can be analyzed for a DNA fingerprint (the subject of the last tutorial). But how do you copy DNA?
The way it’s done is through a technique called the polymerase chain reaction, or PCR.
- Polymerase is the enzyme (DNA polymerase) that copies the DNA.
-
A nuclear chain reaction A chain reaction is a process where the products of the reaction promote or spread the reaction. That leads to an exponentially expanding positive feedback loop. The term “chain reaction” is typically associated with atomic bombs, where the splitting of one atom leads to the spitting of two or more atoms. Since each splitting atom releases energy, the amount of energy released soon rises to an enormously destructive level.
PCR was developed in 1983 by Kary Mullis. Before that, the only way to copy a gene (or any other piece of DNA, indicated by “f” below) was to insert it into a plasmid (c). This would create a plasmid with recombinant DNA (g). This recombinant plasmid would then be inserted into a bacterial cell (h). Every time the cell reproduced (i), it would also replicate the recombinant plasmid.
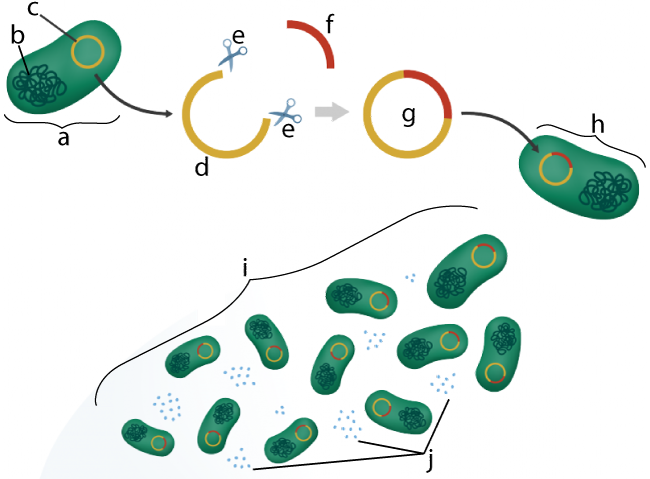
Engineers would then need to extract the plasmids from the cells, apply restriction enzymes to cut out the desired DNA, and isolate the DNA that they were trying to clone.
PCR is much easier. As opposed to what’s above, which requires cells, PCR is what’s called in vitro DNA synthesis. In vitro means “in glass.” In this context, it just means that it can be done in a test tube, without cells.
PCR has become one of the most important techniques in biotechnology. Mullis was awarded the Nobel Prize for this work in 1993. PCR is not only used in forensics (amplifying DNA from a crime scene for analysis), but also in medical and biological research. A widely used test for diagnosing COVID-19 is a PCR test (the link opens in a new browser tab).
2. How PCR Works
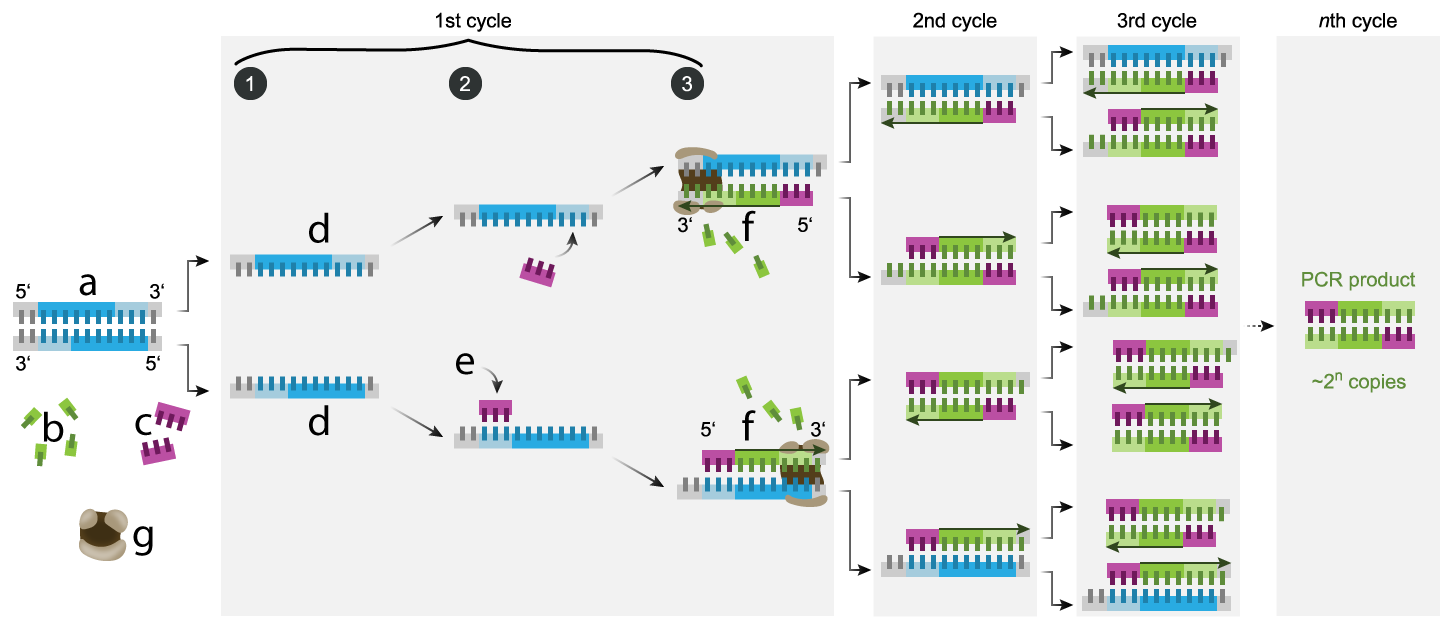
In the diagram above, “a” represents the target DNA that you’re interested in cloning. Along with the target DNA, you’ll need
- primers: short single-stranded segments of DNA that bind with known sequences at the start of the DNA you want to clone. These are shown at “c.” We’ll need primers that bind to the 3′ end of both strands of our target DNA.
- Nucleotide triphosphates (shown at “b”). These are the As, Ts, Cs, and Gs that make up DNA.
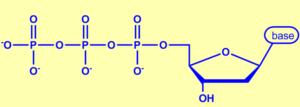
Figure 3: Nucleotide triphosphate - Heat-resistant DNA Polymerase (shown at “g”). DNA polymerase is the enzyme that replicates DNA by adding new nucleotides to the 3′ end of a growing strand. Because PCR involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling, we’ll need DNA polymerase that won’t become denatured at high temperatures. Nature has provided this in the form of Taq polymerase. This is DNA polymerase derived from Thermus aquaticus, a bacterium that lives in hot springs and hydrothermal vents.
Once we’ve assembled our ingredients, we can begin PCR. There are three steps (indicated by the circled 1, 2, and 3 above).
- Denaturation: Heat the DNA to a temperature of 94°C to 96° C. This breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the strands together, rendering the DNA into two single strands (shown at “d.”)
- Annealing: Let the mixture cool to about 68°C. This allows the primers to bind with the single strands of DNA (shown at “e.”)
- Elongation: Once the primer is in place, DNA polymerase will elongate each strand, adding new nucleotides that are complementary to the DNA templates. This is shown at “f.”
Each cycle doubles the amount of DNA. Repeat this a dozen times, and you’ll have 212 more DNA than you started with. That’s a 4096-fold increase. If you repeat 30 times, you’ll have amplified the DNA by 230, which is over a billion-fold.
3. PCR Flashcards
[qdeck bold_text=”false” style=”width: 600px !important; min-height: 450px !important;” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-PCR flashcards (v2.0)”]
[h] PCR
[i]
[start]
[q] Before PCR, what was the only way to copy a gene (or any other piece of DNA)?
[a] Before PCR, the only way to copy a gene (or any other piece of DNA, indicated by “f” below) was to insert it into a plasmid (c). This would create a plasmid with recombinant DNA (g). This recombinant plasmid would then be inserted into a bacterial cell (h). Every time the cell reproduced (i), it would also replicate the recombinant plasmid. Engineers would then need to extract the plasmids from the cells, apply restriction enzymes to cut out the desired DNA, and isolate the DNA that they were trying to clone.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”6.Gene_Expression_and_Regulation” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|16f95379f8510″ question_number=”272″ topic=”6.8.Biotechnology”] What is PCR? What is it used for, and how does it work?
[a] PCR stands for “polymerase chain reaction.” It’s a cell-free technique for cloning DNA. PCR requires the DNA sample that you want to clone (a), primers—short strands of single-stranded DNA that bind to sequences at the start of the DNA that you want to amplify (c), heat-resistant DNA polymerase (not shown), and free nucleotides for DNA synthesis (b). PCR involves repeated cycles of heating the DNA to separate it into single strands (1); then cooling the DNA so that primers can bind and so that DNA polymerase can synthesize new DNA (2 and 3)) Every heating and cooling cycle doubles the amount of DNA. After 10 cycles you have 1000 times more DNA than you started with. After 30 cycles, you’ve amplified your DNA a billionfold.
[x] [restart]
[/qdeck]
4. PCR: Checking Understanding
Complete the following quiz.
[qwiz random = “true” style=”width: 650px !important;” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-PCR Quiz (v2.0)”] [h]
PCR Quiz
[i]
[q] In the diagram below, which number or letter indicates the target DNA that’s about to be amplified?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IG E=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCEgTGV0dGVyICYjODIyMDthJiM4MjIxOyBpcyB0aGUgdGFyZ2V0IEROQS4=[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBKdXN0IGlkZW50aWZ5IHdoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBiZWluZyBjb3BpZWQsIGFuZCB5b3UmIzgyMTc7bGwgaGF2ZSB5b3VyIGFuc3dlci4=[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which letter indicates free nucleotides?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IG I=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCEgTGV0dGVyICYjODIyMDtiJiM4MjIxOyBzaG93cyBmcmVlIG51Y2xlb3RpZGVzLsKg[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBMb29rIGZvciB0aGUgbW9ub21lcnMsIG9yIHVuaXRzLCB0aGF0IGFyZSBnb2luZyB0byBiZSB1c2VkIHRvIGJ1aWxkIG5ldyBETkEu[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which number or letter indicates the primer before it binds with the template DNA?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IG M=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3QhIExldHRlciAmIzgyMjA7YyYjODIyMTsgcmVwcmVzZW50cyBhbiB1bmJvdW5kIHByaW1lci4=[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBMb29rIGZvciBhIHNob3J0IHN0cmluZyBvZiBudWNsZW90aWRlcyB0aGF0IHdpbGwgYmluZCBhdCB0aGUgc3RhcnQgb2YgdGhlIHRhcmdldCBETkEu[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which letter indicates the DNA after it’s been denatured?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IG Q=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3QhIExldHRlciAmIzgyMjA7ZCYjODIyMTsgcmVwcmVzZW50cyBkZW5hdHVyZWQgRE5BIChub3cgdHdvIA==c2luZ2xlIHN0cmFuZHMpLsKg[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBEZW5hdHVyYXRpb24gYnJlYWtzIHRoZSBoeWRyb2dlbiBib25kcyB0aGF0IGhvbGQgdGhlIGRvdWJsZSBoZWxpeCB0b2dldGhlci4gT25jZSB0aG9zZSBib25kcyBhcmUgYnJva2VuLCB3aGF0IHdpbGwgdGhlIEROQSBsb29rIGxpa2U/[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which letter shows a primer binding with the template DNA?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IG U=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3QhIExldHRlciAmIzgyMjA7ZSYjODIyMTsgc2hvd3MgYSBwcmltZXIgYmluZGluZyB3aXRoIHRoZSB0ZW1wbGF0ZSBETkEu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBMb29rIGZvciBhIHNtYWxsIHNlcXVlbmNlIG9mIG51Y2xlb3RpZGVzIHRoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBjb21wbGVtZW50YXJ5IHdpdGggbnVjbGVvdGlkZXMgYXQgdGhlIDMmIzgyNDI7IGVuZCBvZiB0aGUgdGVtcGxhdGUgc3RyYW5kLg==[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which letter indicates newly synthesized DNA?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IG Y=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3QhICYjODIyMDtGJiM4MjIxOyBzaG93cyBuZXdseSBzeW50aGVzaXplZCBETkEu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBMb29rIGZvciB0aGUgYXNzZW1ibHkgb2YgdGhlIGluZGl2aWR1YWwgbnVjbGVvdGlkZXMgKHNob3duIGF0ICYjODIyMDtiJiM4MjIxOykgaW50byBhIGNvbm5lY3RlZCBzdHJhbmQu[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which number or letter indicates DNA polymerase?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE c=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3QhICYjODIyMDtHJiM4MjIxOyBzaG93cyBETkEgcG9seW1lcmFzZQ==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBETkEgcG9seW1lcmFzZSBpcyB0aGUgZW56eW1lIHRoYXQgbWFrZXMgdGhlIG5ldyBETkEuIEl0IHJpZGVzIGFsb25nIGEgdGVtcGxhdGUgc3RyYW5kIG9mIEROQSBhbmQgYXR0YWNoZXMgbmV3IG51Y2xlb3RpZGVzIHRvIHRoZSBncm93aW5nIHN0cmFuZC4gTG9vayBhdCBzdGVwIDMgYW5kIHNlZSBpZiB5b3UgY2FuIGZpbmQgc29tZXRoaW5nIHRoYXQgZml0cyB0aGF0IGRlc2NyaXB0aW9uLg==[Qq]
[q multiple_choice=”true”] In the diagram below, phase 1 is best described as
[c]IGRlbmF0dX JhdGlvbg==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCEgRGVuYXR1cmF0aW9uIGJyZWFrcyB0aGUgaHlkcm9nZW4gYm9uZHMgaG9sZGluZyBETkEgdG9nZXRoZXIsIGJyZWFraW5nIHRoZSBETkEgaW50byB0d28gc2luZ2xlIHN0cmFuZHMu[Qq]
[c]IGFubmVhbGluZw==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiAmIzgyMjA7QW5uZWFsaW5nJiM4MjIxOyBtZWFucyBzdGlja2luZyB0by4mIzgyMjE7IEluIHBoYXNlIDEsIG5vdGhpbmcmIzgyMTc7cyBzdGlja2luZy4gUmF0aGVyIGJvbmRzIGFyZSBiZWluZyBicm9rZW4u[Qq]
[c]IGVsb25nYXRpb24=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBFbG9uZ2F0aW9uIGlzIHdoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBoYXBwZW5pbmcgaW4gc3RlcCAzLg==[Qq]
[q multiple_choice=”true”] In the diagram below, phase 2 is
[c]IGRlbmF0dXJhdGlvbg==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBEZW5hdHVyYXRpb24gYnJlYWtzIHRoZSBoeWRyb2dlbiBib25kcyBob2xkaW5nIEROQSB0b2dldGhlciwgYnJlYWtpbmcgdGhlIEROQSBpbnRvIHR3byBzaW5nbGUgc3RyYW5kcy4gV2hhdCB5b3Ugc2VlIGluIHBoYXNlIHR3byBhcmUgdHdvIHRoaW5ncyBzdGlja2luZyB0b2dldGhlci4=[Qq]
[c]IGFubmVh bGluZw==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gJiM4MjIwO0FubmVhbGluZyYjODIyMTsgbWVhbnMgc3RpY2tpbmcgdG8uJiM4MjIxOyBJbiBwaGFzZSAyLCB0aGUgcHJpbWVyIGlzIHN0aWNraW5nIHRvIHRoZSB0ZW1wbGF0ZSBzdHJhbmRzLg==[Qq]
[c]IGVsb25nYXRpb24=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBFbG9uZ2F0aW9uIGlzIHdoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBoYXBwZW5pbmcgaW4gc3RlcCAzLg==[Qq]
[q multiple_choice=”true”] In the diagram below, phase 3 is
[c]IGRlbmF0dXJhdGlvbg==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBEZW5hdHVyYXRpb24gYnJlYWtzIHRoZSBoeWRyb2dlbiBib25kcyBob2xkaW5nIEROQSB0b2dldGhlciwgYnJlYWtpbmcgdGhlIEROQSBpbnRvIHR3byBzaW5nbGUgc3RyYW5kcy4gV2hhdCB5b3Ugc2VlIGluIHBoYXNlIHRocmVlIGludm9sdmVzIEROQSBwb2x5bWVyYXNlIGFkZGluZyBuZXcgbnVjbGVvdGlkZXMgdGhlIEROQSBtb2xlY3VsZS4=[Qq]
[c]IGFubmVhbGluZw==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiAmIzgyMjA7QW5uZWFsaW5nJiM4MjIxOyBtZWFucyBzdGlja2luZyB0bywmIzgyMjE7IGFuZCBpdCByZWZlcnMgdG8gdGhlIHByaW1lciBzdGlja2luZyB0byB0aGUgdGVtcGxhdGUgc3RyYW5kLg==[Qq]
[c]IGVsb25n YXRpb24=[Qq]
[f]IFdheSB0byBHbyEgRWxvbmdhdGlvbiBpcyB3aGF0JiM4MjE3O3MgaGFwcGVuaW5nIGluIHN0ZXAgMy4=[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which letter indicates annealing?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IG M=[Qq]
[f]WWVzISBMZXR0ZXIgJiM4MjIwO2MmIzgyMjE7IHJlcHJlc2VudHMgYW5uZWFsaW5nLg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiAmIzgyMjA7QW5uZWFsaW5nJiM4MjIxOyBtZWFucyAmIzgyMjA7c3RpY2tpbmcgdG8uJiM4MjIxOyBGaW5kIHdoZXJlIHRoZSBwcmltZXIgaXMgc3RpY2tpbmcgdG8gdGhlIEROQSB0ZW1wbGF0ZS4=[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which letter indicates elongation?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IG Q=[Qq]
[f]WWVzISBMZXR0ZXIgJiM4MjIwO2QmIzgyMjE7IHJlcHJlc2VudHMgZWxvbmdhdGlvbi4=[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBGaW5kIHdoZXJlIEROQSBwb2x5bWVyYXNlIGlzIGNyZWF0aW5nIGFuIGluY3JlYXNpbmdseSBsb25nIHN0cmFuZCBvZiBjb21wbGVtZW50YXJ5IEROQS4=[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which number is pointing to a primer?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID I=[Qq]
[f]TmljZSBqb2IuICYjODIyMDsyJiM4MjIxOyByZXByZXNlbnRzIGEgcHJpbWVyLg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUaGUgcHJpbWVyIGlzIGEgc2hvcnQgc2VxdWVuY2Ugb2Ygc2luZ2xlLXN0cmFuZGVkIEROQSB0aGF0IGJpbmRzIHdpdGggdGhlIDMmIzgyNDI7IGVuZCBvZiB0aGUgdGVtcGxhdGUgRE5BLg==[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which number is pointing to free nucleotides?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID M=[Qq]
[f]WWVzISAmIzgyMjA7MyYjODIyMTsgcmVwcmVzZW50cyBmcmVlIG51Y2xlb3RpZGVzLg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUaGUgZnJlZSBudWNsZW90aWRlcyB3aWxsIGJlIHVzZWQgZHVyaW5nIHRoZSBlbG9uZ2F0aW9uIHBoYXNlIHRvIGNyZWF0ZSBuZXcgc3RyYW5kcyBvZiBETkEu[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which number is pointing to newly synthesized DNA?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID Q=[Qq]
[f]RXhjZWxsZW50LiAmIzgyMjA7NCYjODIyMTsgcmVwcmVzZW50cyBuZXdseSBzeW50aGVzaXplZCBETkEu[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUaGUgbmV3IEROQSBpcyB3aGF0JiM4MjE3O3MgYmVpbmcgc3ludGhlc2l6ZWQgZHVyaW5nIHRoZSBlbG9uZ2F0aW9uIHBoYXNlLg==[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, which number indicates DNA polymerase?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID U=[Qq]
[f]V2F5IHRvIGdvLiBOdW1iZXIgJiM4MjIwOzUmIzgyMjE7IHNob3dzIEROQSBwb2x5bWVyYXNlLg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBETkEgcG9seW1lcmFzZSBpcyB0aGUgZW56eW1lIHRoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBzeW50aGVzaXppbmcgbmV3IEROQSBkdXJpbmcgdGhlIGVsb25nYXRpb24gcGhhc2Uu[Qq]
[q] The image below shows a closeup view of what’s happening during PCR. The primer must be at number
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID E=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCEgVGhlIHByaW1lciBpcyBhdCAmIzgyMjA7MS4mIzgyMjE7[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUaGUgcHJpbWVyIGlzIGEgc2hvcnQgc3RyYW5kIG9mIEROQSB0aGF0IGJpbmRzIHdpdGggdGhlIHRlbXBsYXRlIHN0cmFuZC4=[Qq]
[q] The image below shows a closeup view of what’s happening during PCR. Newly synthesized DNA must be at number
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID M=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0ISBOdW1iZXIgJiM4MjIwOzMmIzgyMjE7IGlzIHRoZSBuZXdseSBzeW50aGVzaXplZCBETkEu[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50OiB0aGUgdGVtcGxhdGUgRE5BIGlzIGF0ICYjODIyMDsyLiYjODIyMTs=[Qq]
[q] The image below shows a closeup view of what’s happening during PCR. DNA polymerase must be at
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID U=[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2QhIEROQSBwb2x5bWVyYXNlIGlzIGF0IG51bWJlciA1LsKg[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBETkEgcG9seW1lcmFzZSBpcyB0aGUgZW56eW1lIHRoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBjb25uZWN0aW5nIGZyZWUgbnVjbGVvdGlkZXMgdG8gY3JlYXRlIG5ldyBETkEu[Qq]
[q] PCR stands for[hangman] [hangman] [hangman]
[c]IHBvbHltZXJhc2U=[Qq]
[c]Y2hhaW4=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[c]IHJlYWN0aW9u[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q] The image below shows a closeup view of what’s happening during PCR. Free nucleotide triphosphates are shown at
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID Q=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0ISBGcmVlIG51Y2xlb3RpZGVzIGFyZSBzaG93biBhdCAmIzgyMjA7NC4mIzgyMjE7[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50OiBmcmVlIG51Y2xlb3RpZGVzIGFyZSBnb2luZyB0byBiZSBpbmNvcnBvcmF0ZWQgaW50byB0aGUgbmV3bHkgc3ludGhlc2l6ZWQgc3RyYW5kLCB3aGljaCBpcyBhdCAmIzgyMjA7My4mIzgyMjE7IFdoYXQgY291bGQgYmUgdGhlIG1vbm9tZXJzIHRoYXQgZ2V0IGluY29ycG9yYXRlZCBpbnRvIHRoYXQgc3RyYW5kPw==[Qq]
[q] During PCR, the highest heat is applied during the[hangman]phase
[c]IGRlbmF0dXJhdGlvbg==[Qq]
[q] During PCR, primers bind to DNA during the [hangman] phase.
[c]IGFubmVhbGluZw==[Qq]
[/qwiz]
5. What’s Next
Proceed to Topic 6.8, Part 4: A few more Genetic Engineering Techniques to Know About: Sequencing and CRISPR
