1. Introduction
In the previous tutorials in this unit, we’ve looked at how water’s polarity and the hydrogen bonding that results affects water’s properties. In this tutorial, we’re going to look at another water-related topic: acids, bases, and the pH scale.
If you’ve taken a previous chemistry course, most of what’s below will be review. And while none of what’s below will show up as questions on the AP Bio exam, it’s important background for understanding many key AP Bio topics.
 2. Solutions, Acids, and Bases
2. Solutions, Acids, and Bases
When you dissolve sugar, salt, or lemonade in water, you’ve made a solution. In a solution, one substance, the solute, is dissolved in another substance, the solvent. In the solution shown in the image to your left, the solute is sugar, and the solvent is water.
In this tutorial, we’re going to focus on two special types of solutions. Acidic solutions have a sour taste. If you have a cut on your skin, and you put an acidic solution on it, it will sting. Strong acids can cause burns, and even dissolve metals. Almost all fruit juices and sodas are acidic. Sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid are two strong acids that you might have heard of.
Basic solutions taste bitter. Strong bases have a soapy feel when you touch them. Unlike acids, bases don’t dissolve metals, so they can be used to unclog pipes by dissolving the hair and other debris that might be clogging them, without dissolving the pipe. Many bleaches and cleaning agents are bases. The word “alkaline” means the same as “basic.”
To see if you’ve mastered the concepts above, take the quiz below.
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Solutions, Acids, and Bases (2.0)”]
[h]Solutions, Acids, and Bases
[i]The following questions include labeling, multiple-choice, and fill-in-the-blanks.
[q]A liquid mixture in which one thing is dissolved in another is a [hangman].
[c]c29sdX Rpb24=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]The thing that does the dissolving in a solution is the [hangman].
[c]c29sdm VudA==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]The thing that gets dissolved in a solution is the [hangman].
[c]c29s dXRl
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A solution with a bitter taste is a(n) [hangman].
[c]YmFz ZQ==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A solution with a sour taste is a(n) [hangman].
[c]YWNp ZA==
Cg==[Qq]
[q][hangman] can dissolve metals
[c]YWNp ZHM=
Cg==[Qq]
[q][hangman] sting when you get them on a cut
[c]YWNp ZHM=[Qq]
[q]Soda drinks are _________
[c]YWNp ZGlj[Qq]
[c]YmFzaWM=[Qq]
[f]TmljZS7CoFNvZGEgZHJpbmtzIGFyZSBhY2lkaWMu[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFNvZGEgZHJpbmtzIGhhdmUgYSBzb3VyIHRhc3RlLiBTb3VyIGxpcXVpZHMgYXJlIF9fX19fXy4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q][hangman] have a bitter taste.
[c]YmFz ZXM=
Cg==[Qq]
[q][hangman] have a slippery or soapy feel
[c]YmFz ZXM=[Qq]
[q labels = “right”]
[l]solvent
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]solute
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[q]A word that means the same as basic is [hangman].
[c]YWxrYW xpbmU=[Qq]
[x][restart]
[/qwiz]
3. The Chemistry of Acids and Bases: What Biology Students Need to Know
What causes a solution to be acidic or basic? A water molecule, or H20, can dissociate, or fall apart, to form two charged particles or ions. One of these ions is called a “hydrogen ion,” written as H+ (and pronounced “H-plus”). An H+ is simply a proton, floating around in a solution. The other ion is written as OH– (which is pronounced as “O” “H” minus). The OH– ion is also called “hydroxide.” Here’s the equation for the dissociation of water.
H2O → H+ + OH–
In a chemistry class, you’ll learn that the H+ immediately combines with a water molecule to form H3O+, also known as the hydronium ion. For biology students, it’s very useful to continue to think of water as dissociating into H+ and OH–
If dissolving something in water causes it to have more H+ than OH–, then the solution is acidic. For example, if the compound HCl (hydrochloric acid) is dissolved in water, the hydrogen ions dissociate from the chlorine as shown below:
HCl→H+ + Cl–
The added H+ ions make the resulting solution an acid.
Conversely, if dissolving something in water causes it to have more OH– than H+, then the resulting solution is a base. For example, when Sodium Hydroxide (lye) is dissolved in water, the sodium dissociates from the hydroxide ion:
NaOH → Na+ + OH–
If the amount H+ is equal to OH–, then the solution is neutral. Pure water has a pH of 7, but what comes out of the tap is usually a weak acid.
Acidic and basic solutions are measured on the pH (pronounced “P” “H”) scale. On the pH scale, the acids with the most hydrogen ions are at 0 (or rarely, below 0). The most concentrated bases are at pH 14 (or above). A neutral liquid is 7.
The scale works by powers of 10, so a solution with pH 5 is 10 times more acidic than a solution that is pH 6. A solution that is pH 12 is 10 times more basic than a solution that is pH 11.
Here’s a graphical version of the pH scale.
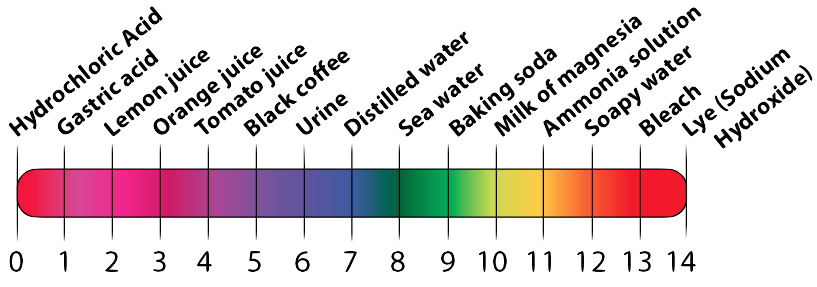
4. Acids, Bases, and pH: Checking Understanding
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Acids, Bases, and pH”]
[h]Quiz: Acids, Bases, and pH
[i]
[q]The change of a water molecule into an H+ and an OH– is called [hangman].
[c]ZGlzc29jaWF0aW9u
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Another word for the H+ ion is [hangman] ion.
[c]aHlkcm9nZW4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A solution with more H+ than OH– is a(n) [hangman].
[c]YWNpZA==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A solution with more than OH– than H+ is a(n) [hangman].
[c]YmFzZQ==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A solution with pH 9 is a(n) [hangman].
[c]YmFzZQ==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A solution with pH 4 is a(n) [hangman].
[c]YWNpZA==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A solution with pH 7 is
[c]YWNpZGlj[Qq]
[c]YmFzaWM=[Qq]
[c]bmV1dH JhbA==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRha2UgYSBsb29rIGF0IHRoaXMgZGlhZ3JhbSwgYW5kIG5vdGljZSB3aGVyZSA3IGxpZXMu
Cg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRha2UgYSBsb29rIGF0IHRoaXMgZGlhZ3JhbSwgYW5kIG5vdGljZSB3aGVyZSA3IGxpZXMu
Cg==[Qq]
[f]Q29ycmVjdMKgLkHCoHNvbHV0aW9uwqBwSCA3wqBpc8KgbmV1dHJhbC4=
Cg==Cg==[Qq]
[q labels = “top”]Label the following.
| ph 6 | pH 8 |
| ____________ | ____________ |
[l]more acidic
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]more basic
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[q labels = “top”]Compare the following:
| ph 3 | pH 5 |
| ____________ | ____________ |
[l]more H+
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]more OH–
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[q labels = “top”]Label the following.
| ph 3 | pH 9 |
| ____________ | ____________ |
[l]less basic
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]more basic
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[q]Compared to a solution that’s pH 3, a solution that’s pH 1 is ___ times more acid.
[c]dHdpY2U=[Qq]
[c]dGhyZWUgdGltZXM=[Qq]
[c]dGVuIHRpbWVz[Qq]
[c]MTAwIH RpbWVz[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoZSBwSCBzY2FsZSB3b3JrcyBieSBwb3dlcnMgb2YgMTAgKG11Y2ggbGlrZSB0aGUgUmljaHRlciBzY2FsZSBmb3IgZWFydGhxdWFrZSBtYWduaXR1ZGUpLiBGb3IgZXhhbXBsZSwgYSBwSCBvZiA1IGlzIDEwIHRpbWVzIGZvciBhY2lkaWMgdGhhbiBhIHBIIG9mIDYuIFVzZSB0aGlzIHRvIGZpZ3VyZSBvdXQgdGhlIGRpZmZlcmVuY2UgaW4gYWNpZGl0eSBiZXR3ZWVuIHBIIDEgYW5kIHBoIDMu[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoZSBwSCBzY2FsZSB3b3JrcyBieSBwb3dlcnMgb2YgMTAgKG11Y2ggbGlrZSB0aGUgUmljaHRlciBzY2FsZSBmb3IgZWFydGhxdWFrZSBtYWduaXR1ZGUpLiBGb3IgZXhhbXBsZSwgYSBwSCBvZiA1IGlzIDEwIHRpbWVzIGZvciBhY2lkaWMgdGhhbiBhIHBIIG9mIDYuIFVzZSB0aGlzIHRvIGZpZ3VyZSBvdXQgdGhlIGRpZmZlcmVuY2UgaW4gYWNpZGl0eSBiZXR3ZWVuIHBIIDEgYW5kIHBoIDMu[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoZSBwSCBzY2FsZSB3b3JrcyBieSBwb3dlcnMgb2YgMTAgKG11Y2ggbGlrZSB0aGUgUmljaHRlciBzY2FsZSBmb3IgZWFydGhxdWFrZSBtYWduaXR1ZGUpLiBGb3IgZXhhbXBsZSwgYSBwSCBvZiA1IGlzIDEwIHRpbWVzIGZvciBhY2lkaWMgdGhhbiBhIHBIIG9mIDYuIFVzZSB0aGlzIHRvIGZpZ3VyZSBvdXQgdGhlIGRpZmZlcmVuY2UgaW4gYWNpZGl0eSBiZXR3ZWVuIHBIIDEgYW5kIHBoIDMu[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBUaGUgcEggc2NhbGUgd29ya3MgYnkgcG93ZXJzIG9mIDEwIChtdWNoIGxpa2UgdGhlIFJpY2h0ZXIgc2NhbGUgZm9yIGVhcnRocXVha2UgbWFnbml0dWRlKSBBIHBIIG9mIDEgaXMgMTAwWCBtb3JlIGFjaWRpYyB0aGFuIGEgcEggb2YgMy4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Compared to a solution that’s pH 7, a solution that’s pH 8 is ___ times more basic.
[c]dHdpY2U=[Qq]
[c]dGhyZWUgdGltZXM=[Qq]
[c]dGVuIH RpbWVz[Qq]
[c]MTAwIHRpbWVz[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoZSBwSCBzY2FsZSB3b3JrcyBieSBwb3dlcnMgb2YgMTAgKG11Y2ggbGlrZSB0aGUgUmljaHRlciBzY2FsZSBmb3IgZWFydGhxdWFrZSBtYWduaXR1ZGUpLiBVc2UgdGhhdCB0byBmaWd1cmUgb3V0IGhvdyBtdWNoIG1vcmUgYmFzaWMgOCBpcyB0aGFuIDcu[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoZSBwSCBzY2FsZSB3b3JrcyBieSBwb3dlcnMgb2YgMTAgKG11Y2ggbGlrZSB0aGUgUmljaHRlciBzY2FsZSBmb3IgZWFydGhxdWFrZSBtYWduaXR1ZGUpLiBVc2UgdGhhdCB0byBmaWd1cmUgb3V0IGhvdyBtdWNoIG1vcmUgYmFzaWMgOCBpcyB0aGFuIDcu[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBUaGUgcEggc2NhbGUgd29ya3MgYnkgcG93ZXJzIG9mIDEwLiBTbyBhIHNvbHV0aW9uIHRoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBwSCA4IGlzIDEwIHRpbWVzIG1vcmUgYmFzaWMgdGhhbiBvbmVzIHRoYW4gb25lIHRoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBwSCA3Lg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoZSBwSCBzY2FsZSB3b3JrcyBieSBwb3dlcnMgb2YgMTAgKG11Y2ggbGlrZSB0aGUgUmljaHRlciBzY2FsZSBmb3IgZWFydGhxdWFrZSBtYWduaXR1ZGUpLiBVc2UgdGhhdCB0byBmaWd1cmUgb3V0IGhvdyBtdWNoIG1vcmUgYmFzaWMgOCBpcyB0aGFuIDcu
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A solution that is 1000 times less basic than a solution that is pH 12 would have a pH of ___
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]OQ ==[Qq]
[f]RXhjZWxsZW50LiBBIHNvbHV0aW9uIHRoYXQgaXMgMTAwMCB0aW1lcyBsZXNzIGJhc2ljIHRoYW4gYSBzb2x1dGlvbiB0aGF0IGlzIHBIIDEyIHdvdWxkIGhhdmUgYSBwSCBvZsKgOS4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEVhY2ggZGVjcmVhc2UgaW4gcEggbnVtYmVyIHJlcHJlc2VudHMgYSAxMCB0aW1lcyBkZWNyZWFzZSBpbiBhY2lkaXR5LiBTbywgcGggMTEgaXMgMTAgdGltZXMgbGVzcyBiYXNpYyB0aGFuIDEyLCBhbmQgcEggMTAgaXMgMTAwIHRpbWVzIGxlc3MgYmFzaWMgdGhhbiAxMi4gV2hhdCBwSCBpcyAxMDAwIHRpbWVzIGxlc3MgYmFzaWMgdGhhbiAxMj8=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A solution that is 100 times less acidic than a solution that is pH 2 would have a pH of ___
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]NA ==[Qq]
[f]RXhjZWxsZW50LiBBIHNvbHV0aW9uIHRoYXQgaXMgMTAwIHRpbWVzIGxlc3MgYWNpZGljwqB0aGFuIGEgc29sdXRpb24gdGhhdCBpcyBwSCAyIHdvdWxkIGhhdmUgYSBwSCBvZiA0Lg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEVhY2ggaW5jcmVhc2XCoGluIHBIIG51bWJlciByZXByZXNlbnRzIGEgMTAgdGltZXMgZGVjcmVhc2UgaW4gYWNpZGl0eS7CoFNvLCBwaCAzwqBpcyAxMCB0aW1lcyBsZXNzIGFjaWRpY8KgdGhhbiBwSCAyLsKgV2hhdCBwSCBpcyAxMDAgdGltZXMgbGVzcyBhY2lkaWPCoHRoYW4gcEggMj8=[Qq]
[/qwiz]
5. Buffers
A buffer is a substance that when added to a solution, enables that solution to resist changes in pH when an acid or a base is added to it (source: slightly modified from the New Oxford American Dictionary). Blood, for example, resists changes in its pH much more than an equivalent quantity of water. That’s because blood contains buffers that are capable of soaking up hydrogen ions (H+) when acids enter the blood, and which release hydrogen ions when blood’s pH starts to rise.
One of the buffers which enables blood to do this is carbonic acid. The formula for carbonic acid is H2CO3. Carbonic acid can dissociate by losing a hydrogen ion, making it into the bicarbonate ion (HCO3–), which is a base. You can see this in the chemical reaction below.
H2CO3 → HCO3– + H+
Carbonic acid itself is a weak acid. When added to water, a small amount of carbonic acid will dissociate and release H+ into the solution (which is why it’s an acid). But if another acid is added to the same solution, then the H+ released by the second acid will combine with the bicarbonate ion, creating more carbonic acid. Because carbonic acid is a buffer, that decreases the pH of the solution (making it less acidic) by absorbing the H+. By contrast, when a base is added to the solution (causing the pH to rise), more carbonic acid will dissociate, releasing H+ into the solution, causing the pH to fall.
6. Conclusion: Acids, Bases, pH, and Life
Acids and bases are incredibly important to understanding how living things work. One of the most important aspects of homeostasis in any organism is keeping the pH in a cell’s cytoplasm, outside the cell, and or within a body compartment (the stomach, or the inside of a blood vessel) within a very specific range. Exceeding that range, even by a little bit, can be harmful or fatal. We’ve seen above how buffers help maintain the pH of the blood. We’ll continue to see, throughout this course, the variety of adaptations that organisms have for controlling pH.
7. Topic 1.1 Flashcards: Water and Hydrogen Bonding
[qdeck bold_text=”false” random=”true” style=”min-height: 450px !important; width: 550px !important;” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Topic 1.1 (Water) Cumulative Flashcards (2.0)”]
[h] Topic 1.1 (Chemistry of Water) Flashcards
[i]
[start]
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2015b50167510″ question_number=”1″ topic=”1.1.Structure_of_Water_and_Hydrogen_Bonding”] Describe hydrogen bonding in water.
[a] Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular bonds that form between the partially positive (hydrogen) side of one water molecule and the partially negative (oxygen) side of another water molecule.
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|21e12b9c37086e” question_number=”2″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.1.Structure_of_Water_and_Hydrogen_Bonding”] Using the diagram below as an example, describe how hydrogen bonds can form between molecules besides water.
[a] Hydrogen bonds can form between partially positive and partially negatively charged regions of any molecule. In the image below, there are two hydrogen bonds. In the one on top, the hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge and the oxygen is partially negative. In the one below, the nitrogen is partially negative, and the hydrogen is partially positive.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1ff66ba19f910″ question_number=”3″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.1.Structure_of_Water_and_Hydrogen_Bonding”] What is heat of vaporization? Why does water have a very high heat of vaporization, and how do organisms exploit this to regulate body temperature?
[a] Heat of vaporization is the energy required to transform a liquid into a gas. Because the breaking of hydrogen bonds requires energy, water has a very high heat of vaporization. That means that when water is converted into water vapor (which happens when sweat evaporates from human skin or from a dog’s tongue), it carries away a lot of heat energy, lowering the temperature of the body that it evaporated from. This is how evaporative cooling works, and it’s a key thermoregulatory adaptation in humans and other animals.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.1.Structure_of_Water_and_Hydrogen_Bonding” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|10288513b6357e” question_number=”4″] Describe cohesion, adhesion and surface tension, and explain how these key properties of water result from hydrogen bonding.
[a] Cohesion involves hydrogen bonds between water molecules. It’s responsible for water’s high heat of vaporization, high specific heat, and high surface tension. Surface tension is the force exerted by the water molecules on the surface of a body of water. This creates a kind of web or net upon which insects like water striders can stand, and which also resists evaporation. Adhesion involves hydrogen bonds between water molecules and other polar substances, such as the cellulose walls making up the xylem of plants. Adhesion is responsible for capillary action. Working together, evaporation, cohesion, and adhesion make it possible for trees to pull water from their roots up to their leaves.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1fecabafd4d10″ question_number=”5″ topic=”1.1.Structure_of_Water_and_Hydrogen_Bonding”] In terms of hydrogen ions, hydroxide ions, and pH, describe the difference between an acidic and a basic solution.
[a] Acidic solutions have more hydrogen ions (protons or H+) than hydroxide ions (represented by OH–) The pH of an acidic solution is below 7. Bases are substances that have more hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions, and their pH is above 7.
[/qdeck]
What now?
- This is the last tutorial in this series about the Chemistry of Water and Hydrogen Bonding. The next AP Bio topic is Topic 1.2, Carbon and the Elements of Life.
