1. Watch these Videos
1.a. Calvin Cycle Explained for AP Bio
1.b. Calvin Cycle Rap (Music Video)
2. Study this Summary
Note: the explanation below keeps track of the number of carbon atoms at each step of the process. Doing this kind of “carbon accounting” will really help you understand what happens during the Calvin Cycle
Overview of the Calvin Cycle
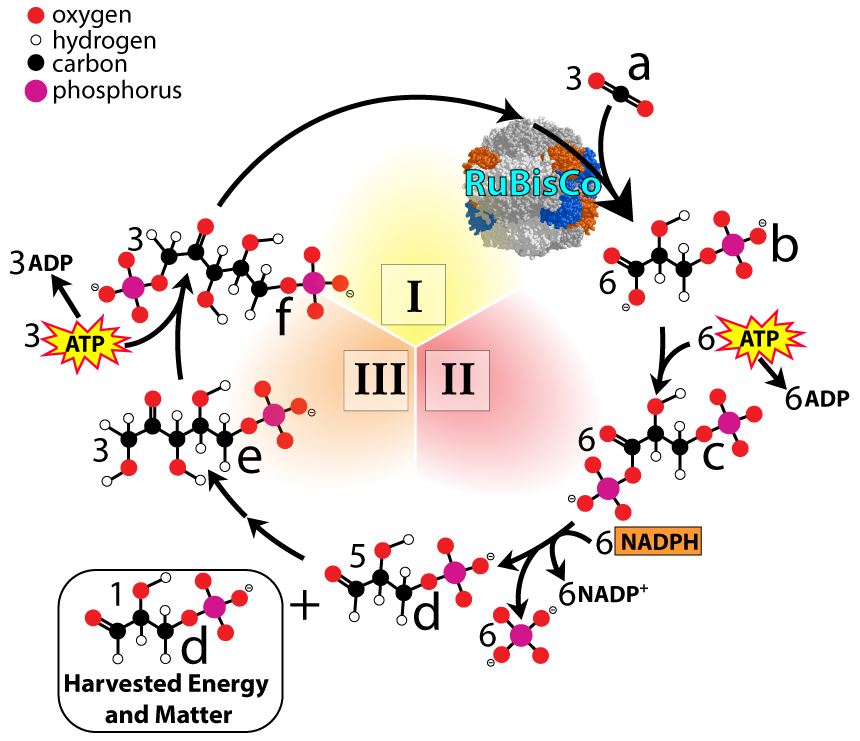
- The Calvin cycle uses the products of the light reactions (ATP and NADPH) and carbon dioxide to synthesize G3P, a precursor for synthesizing sugars and other compounds.
- Note: many older sources use the acronym PGAL (phosphoglyceraldehyde) instead of G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate).
- The process occurs in three phases:
- I: Carbon Fixation: CO2 is incorporated into the biosphere as it combines with RuBP. RuBP is the cycle’s starting and ending point.
- II: Energy Investment and Harvest: ATP and NADPH are used to create G3P, a 3-Carbon molecule that can be enzymatically converted into glucose (or anything else the cell needs).
- ATP provides the energy to drive this endergonic reaction forward.
- NADPH provides the reducing power to create the reduced, high energy molecule G3P. The reduction of G3P is coupled to the oxidation of NADPH to NADP+
- III Regeneration of RuBP: G3P molecules are reorganized into RuBP, allowing the cycle to continue.
Phase 1: Carbon Fixation
- The enzyme Rubisco combines CO2 with RuBP (a 5-carbon compound) to form an unstable 6-carbon product.
- The 6-carbon product immediately splits into two 3-carbon molecules (b, above)
- Carbon Accounting
- Carbon fixation starts with 3 RuBP molecules (15 carbons)
- 3 CO2 molecules (3 carbons) are added to the 3 RuBPs, momentarily creating 3 6-carbon molecules (with 18 carbons)
- The dissociation of these three 6-carbon molecules into six 3-carbon compounds (b above) keeps the carbon count at 18.
Phase 2: Energy Investment and Harvest
- Phosphorylation: Enzymes take a phosphate group from ATP and add it to the 3-carbon intermediate compound. This is shown at “c” above.
- Reduction: Enzymes use electrons from NADPH to reduces one of these 3-carbon intermediates to G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate), a high-energy molecule (shown at “d”)
- One G3P is removed at the end of this phase.
- Carbon Accounting
- Phosphorylation and reduction of these six G3P molecules doesn’t change the carbon count, which stays at 18 carbons.
- Harvest of one G3P molecule (with three carbon atoms) reduces the carbon count by three, so the investment and harvest phase ends with 5 G3Ps, with a total of 15 carbons.
Phase 3: Regeneration of RuBP
- Enzymes rearrange the three-carbon G3Ps into five-carbon RuBPs. This process involves a phosphorylation, as phosphates from ATP are used to synthesize the RuBP.
- Carbon Accounting:
- Five G3P molecules (with a total of 15 carbons) are rearranged into 3 molecules of RuBP. RuBP has 5 carbons, so the cycle ends with 15 carbon atoms (which are used to start the next cycle).
Key Points About the Calvin Cycle
- The Calvin cycle is a cycle! It starts and ends with 5-carbon RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate).
- Its harvestable product is G3P: A high-energy molecule that forms the basis for sugars and other biomolecules.
- It relies on ATP and NADPH generated during the light reactions.
- Various reactions in the Calvin cycle create ADP, Pi, and NADP+, which are inputs for the light reactions.
- The Calvin cycle brings inorganic carbon (from carbon dioxide) into the biosphere, a process known as carbon fixation. Almost all the carbon in the biosphere – including the carbon in you – was once carbon dioxide in the air. You’re here because of the Calvin cycle!
3. Master these Flashcards
[qdeck qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Calvin Cycle Flashcards, APBVP”]
[h] The Calvin Cycle
[i]
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1c502ffe82910″ question_number=”118″ topic=”3.5.Photosynthesis”] Where does the Calvin cycle occur, what does it produce, and how?
[a] The Calvin Cycle occurs in the stroma (the fluid in between the thylakoids and the chloroplasts’ inner membrane). Using the products of the light reactions (ATP and NADPH) and carbon dioxide, the cycle creates the reduced 3-carbon compound G3P, which is converted by other enzymes into carbohydrates (or anything else a plant cell needs).
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1c45b5c900910″ question_number=”119″ topic=”3.5.Photosynthesis”] List the three phases of the Calvin cycle.
[a]
- Carbon fixation phase
- Energy investment and harvest
- Regeneration of RuBP
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” topic=”3.5.Photosynthesis” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1148f750b64a19″ question_number=”120″] Describe what happens during the carbon fixation phase of the Calvin cycle.
[a] During the carbon fixation phase, carbon dioxide is combined with a five-carbon molecule called RuBP. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme RuBisCo. The six-carbon product of this reaction immediately dissociates into two 3 carbon molecules.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” topic=”3.5.Photosynthesis” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|11483610db5e19″ question_number=”121″] Describe what happens during the energy investment and harvest phase of the Calvin cycle.
[a] During investment and harvest (II), the three-carbon products (b) of carbon fixation are reduced and phosphorylated into six molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (d: AKA G3P or PGAL). The energy comes from the ATP and NADPH from the light reactions. One of these G3Ps is then harvested (removed from the cycle).
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” topic=”3.5.Photosynthesis” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|114735f3bf6619″ question_number=”122″] Describe what happens during the last phase of the Calvin cycle.
[a] The last phase is the regeneration of RuBP. During this phase, the remaining five G3Ps are rearranged into three 5-carbon RuBPs, the compound that acts as one of the substrates during the carbon fixation phase (the other substrate being carbon dioxide).
[/qdeck]
4. Tackle these Quizzes
4.1. Photosynthesis and the Calvin Cycle
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Photosynthesis and Calvin Cycle, APBVP”]
[h]Photosynthesis and Calvin Cycle
[i]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Part 5 (Calvin Cycle) Introduction|171ddd77ccc756″ question_number=”1″]Photosynthesis involves two phases. The one indicated by “II” is called the [hangman] cycle.
[c]Q2Fsdmlu
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Part 5 (Calvin Cycle) Introduction|171d9e9a8bbb56″ question_number=”2″]The Calvin cycle takes the outputs of the light reactions, and along with carbon dioxide, uses them as inputs. Which number indicates carbon dioxide?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]Ng ==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiDigJw24oCdIGlzIGNhcmJvbiBkaW94aWRl[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIEZpbmQgYW4gYXJyb3cgdGhhdCYjODIxNztzIGdvaW5nIGludG8gdGhlIENhbHZpbiBjeWNsZSwgYnV0IHdoaWNoIGlzIG5vdCBvbmUgb2YgdGhlIG91dHB1dHMgb2YgdGhlIGxpZ2h0IHJlYWN0aW9ucy4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Part 5 (Calvin Cycle) Introduction|171d6211569356″ question_number=”3″]Carbon dioxide, at “6,” can be considered the external input of the Calvin cycle. An internal input includes the reduced mobile electron carrier [hangman], which is shown at “5.”
[c]TkFEUEg=
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Part 5 (Calvin Cycle) Introduction|171d2588216b56″ question_number=”4″]One of the internal inputs of the Calvin cycle is the reduced mobile electron carrier NADPH, shown at “5” below. The other input is [hangman], indicated by “4.”
[c]QVRQ
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Part 5 (Calvin Cycle) Introduction|171ce8feec4356″ question_number=”5″]While the light reactions occur in the thylakoid sacs, the Calvin cycle occurs in the [hangman].
[c]c3Ryb21h
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Part 5 (Calvin Cycle) Introduction|171ca7cd9f5356″ question_number=”6″]Which letter or number shows the structures that carry out the light reactions?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]YQ ==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBUaGUgbGV0dGVyIOKAnGHigJ0gaW5kaWNhdGVzIHRoZSB0aHlsYWtvaWRz[Qq]
[c]SQ ==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiAmIzgyMjA7SSYjODIyMTsgc2hvd3MgYSBzdGFjayBvZiB0aHlsYWtvaWRzIChhbmQgaW5kaWNhdGVzIHRoZSBsaWdodCByZWFjdGlvbnMpLg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIFRoZSBsaWdodCByZWFjdGlvbnMgb2NjdXIgaW4gdGhlIHRoeWxha29pZCBzYWNzLCB3aGljaCBhcmUgdGlueSBvdmFsIHN0cnVjdHVyZXMgd2l0aGluIHRoZSBjaGxvcm9wbGFzdCwgb3JnYW5pemVkIGludG8gc3RhY2tzLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Part 5 (Calvin Cycle) Introduction|171c68f05e4756″ question_number=”7″]Which letter or number shows the area in the chloroplast where the Calvin cycle takes place? (Note: don’t enter a roman numeral)
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]Yg ==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBMZXR0ZXIg4oCcYuKAnSBpbmRpY2F0ZXMgdGhlIHN0cm9tYSwgd2hpY2ggaXMgd2hlcmUgdGhlIENhbHZpbiBjeWNsZSB0YWtlcyBwbGFjZS4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIFRoZSBDYWx2aW4gY3ljbGUgb2NjdXJzIGluIHRoZSBlcXVpdmFsZW50IG9mIHRoZSBjeXRvcGxhc20gb2YgdGhlIGNobG9yb3BsYXN0JiM4MjExO3RoZSBmbHVpZCB0aGF0IGlzIGJldHdlZW4gdGhlIHRoeWxha29pZHMgYW5kIHRoZSBjaGxvcm9wbGFzdCYjODIxNztzIGlubmVyIG1lbWJyYW5lLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Part 5 (Calvin Cycle) Introduction|171c256b057356″ question_number=”8″]To the extent that any biological process can be said to have a purpose, then the purpose of photosynthesis, from a plant’s perspective, is to create
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]Nw ==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBMZXR0ZXIg4oCcN+KAnSBpbmRpY2F0ZXMgY2FyYm9oeWRyYXRlLiBTeW50aGVzaXppbmcgY2FyYm9oeWRyYXRlcyBpcywgZnJvbSBhIHBsYW50JiM4MjE3O3MgcGVyc3BlY3RpdmUsIHRoZSBwdXJwb3NlIG9mIHBob3Rvc3ludGhlc2lzLg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIFRoZSBwdXJwb3NlIG9mIHBob3Rvc3ludGhlc2lzLCBmcm9tIGEgcGxhbnQmIzgyMTc7cyBwZXJzcGVjdGl2ZSwgaXMgdG8gY3JlYXRlIHN1Z2FycyB0aGF0IGNhbiBiZSB1c2VkIGZvciBncm93dGggYW5kIGVuZXJneS4gV2hpY2ggcGFydCBvZiB0aGUgZGlhZ3JhbSBjb3VsZCByZXByZXNlbnQgYSBzdWdhcj8=[Qq]
[x][restart]
[/qwiz]
4.2. The Calvin Cycle (the details)
[qwiz random = “true” width:700px qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Calvin Cycle: The Details, APBVP”]
[h]Calvin Cycle: The Details
[i]
[q labels = “top” dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Calvin Cycle Quiz|171a2e80fd1356″ question_number=”1″]
[l]Carbon Dioxide
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[l]Carbon Fixation Phase
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[l]Energy Investment Phase
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[l]G3P
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]Phosphorylation
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]Reduction
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]RuBP
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[l]RuBP Regeneration Phase
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Calvin Cycle Quiz|1719f69fdfb356″ question_number=”2″]After carbon dioxide is combined with RuBP, the six carbon product immediately dissociates into which of the molecules shown below?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]Yg ==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBMZXR0ZXIg4oCcYuKAnSBpbmRpY2F0ZXMgdGhlIHRocmVlLWNhcmJvbiBtb2xlY3VsZSB0aGF0IGFwcGVhcnMgaW4gdGhlIENhbHZpbiBjeWNsZSBpbW1lZGlhdGVseSBmb2xsb3dpbmcgY2FyYm9uIGZpeGF0aW9uLg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIFVzZSB0aGUgbGVnZW5kICh1cHBlciByaWdodCkgdG8gZmlndXJlIG91dCB3aGljaCBtb2xlY3VsZSBpcyBjYXJib24gZGlveGlkZS4gUmlnaHQgbmVhcmJ5LCB5b3UmIzgyMTc7bGwgZmluZCB5b3VyIGFuc3dlci4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Calvin Cycle Quiz|1719bebec25356″ question_number=”3″]Which letter in the diagram below indicates RuBP, the starting and ending compound in the Calvin cycle?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]Zg ==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBMZXR0ZXIg4oCcZuKAnSBpbmRpY2F0ZXMgUnVCUCwgdGhlIENhbHZpbiBjeWNsZSYjODIxNztzIHN0YXJ0aW5nIGFuZCBlbmRpbmcgY29tcG91bmQ=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIFVzZSB0aGUgbGVnZW5kICh1cHBlciByaWdodCkgdG8gZmlndXJlIG91dCB3aGljaCBtb2xlY3VsZSBpcyBjYXJib24gZGlveGlkZS4gUnVCUCBpcyB0aGUgbW9sZWN1bGUgdGhhdCBnZXRzIGNvbWJpbmVkIHdpdGggY2FyYm9uIGRpb3hpZGUgYXMgdGhlIENhbHZpbiBjeWNsZSBiZWdpbnMu
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Calvin Cycle Quiz|17197d8d756356″ question_number=”4″]Which letter in the diagram below shows a molecule that results from the chemical reduction that occurs within the Calvin cycle?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ZA ==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBMZXR0ZXIg4oCcZOKAnSBpbmRpY2F0ZXMgRzNQLCB3aGljaCByZXN1bHRzIHdoZW4gY29tcG91bmQgJiM4MjIwO2MmIzgyMjE7IGdldHMgcmVkdWNlZCwgcmVjZWl2aW5nIGVsZWN0cm9ucyBhbmQgaHlkcm9nZW4gZnJvbSBOQURQSC4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIFRoZSBiaW9sb2dpY2FsIHJlZHVjdGlvbnMgaW4gdGhlIENhbHZpbiBjeWNsZSBpbnZvbHZlIGVsZWN0cm9ucyBhbmQgaHlkcm9nZW5zIHRoYXQgYXJlIGNvbnRyaWJ1dGVkIGJ5IE5BRFBILiBGaW5kIE5BRFBILCBhbmQgeW91JiM4MjE3O2xsIGhhdmUgeW91ciBhbnN3ZXIu
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Calvin Cycle Quiz|171945ac580356″ question_number=”5″]Which of the phases of the Calvin cycle involves carbon fixation?
[c]SSDCoC DCoCA=[Qq][c]SUkgwqAgwqAg[Qq][c]SUlJ
Cg==[Qq][f]WWVzLiBQaGFzZSBJIG9mIHRoaXMgQ2FsdmluIGN5Y2xlIGRpYWdyYW0gaW52b2x2ZXMgY2FyYm9uIGZpeGF0aW9uLg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoaXMgaXMgdGhlIGVuZXJneSBpbnZlc3RtZW50IHBoYXNlLiBUaGVyZSBhcmUgcmVkdWN0aW9ucyBhbmQgcGhvc3Bob3J5bGF0aW9ucywgYnV0IG5vIGNhcmJvbiBmaXhhdGlvbi4gTG9vayBmb3IgYSBwaGFzZSB3aGVyZSBjYXJib24gaXMgY29taW5nIGludG8gdGhlIGN5Y2xlLg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoaXMgaXMgdGhlIFJ1QlAgcmVnZW5lcmF0aW9uIHBoYXNlLiBMb29rIGZvciBhIHBoYXNlIHdoZXJlIGNhcmJvbiBpcyBjb21pbmcgaW50byB0aGUgY3ljbGUu
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Calvin Cycle Quiz|17190b772ebf56″ question_number=”6″]Which of the phases of the Calvin cycle shown below involves energy investment?
[c]SSDCoCDCoCA=[Qq][c]SUkgwq AgwqAg[Qq][c]SUlJ
Cg==[Qq][f]Tm8uIFBoYXNlIEkgb2YgdGhpcyBDYWx2aW4gY3ljbGUgZGlhZ3JhbSBpbnZvbHZlcyBjYXJib24gZml4YXRpb24uIExvb2sgZm9yIHRoZSBwaGFzZSB3aGVyZSBlbmVyZ3kgdHJhbnNmZXIgbW9sZWN1bGVzIChzdWNoIGFzIEFUUCBhbmQgTkFEUEgpIGFyZSBjb252ZXJ0ZWQgaW50byBsb3dlci1lbmVyZ3kgZm9ybXMu[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBUaGlzIGlzIHRoZSBlbmVyZ3kgaW52ZXN0bWVudCBwaGFzZS4gVGhlcmUgYXJlIHJlZHVjdGlvbnMgYW5kIHBob3NwaG9yeWxhdGlvbnMsIGJvdGggb2Ygd2hpY2ggYWRkIGVuZXJneSB0byB0aGUgbW9sZWN1bGVzIGluIHRoZSBDYWx2aW4gY3ljbGUu[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoaXMgaXMgdGhlIFJ1QlAgcmVnZW5lcmF0aW9uIHBoYXNlLiBMb29rIGZvciB0aGUgcGhhc2Ugd2hlcmUgZW5lcmd5IHRyYW5zZmVyIG1vbGVjdWxlcyAoc3VjaCBhcyBBVFAgYW5kIE5BRFBIKSBhcmUgY29udmVydGVkIGludG8gbG93ZXItZW5lcmd5IGZvcm1zLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_Calvin Cycle Quiz|1718d396115f56″ question_number=”7″]Which of the phases of the Calvin cycle shown below involves regeneration of RuBP?
[c]SSDCoCDCoCA=[Qq][c]SUkgwqAgwqAg[Qq][c]SU lJ
Cg==[Qq][f]Tm8uIFBoYXNlIEkgb2YgdGhpcyBDYWx2aW4gY3ljbGUgZGlhZ3JhbSBpbnZvbHZlcyBjYXJib24gZml4YXRpb24uIExvb2sgZm9yIGEgcGhhc2Ugd2hlcmUgdGhlIHN0YXJ0aW5nIGNvbXBvdW5kICh0aGUgNSBjYXJib24gbW9sZWN1bGUgUnVCUCkgaXMgYmVpbmcgcmVnZW5lcmF0ZWQu[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoaXMgaXMgdGhlIGVuZXJneSBpbnZlc3RtZW50IHBoYXNlLiBMb29rIGZvciBhIHBoYXNlIHdoZXJlIHRoZSBzdGFydGluZyBjb21wb3VuZCAodGhlIDUgY2FyYm9uIG1vbGVjdWxlIFJ1QlApIGlzIGJlaW5nIHJlZ2VuZXJhdGVkLg==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBUaGlzIGlzIHRoZSBSdUJQIHJlZ2VuZXJhdGlvbiBwaGFzZS4=[Qq]
[q]In the diagram below, compound “a” is [hangman] [hangman].
[c]Y2FyYm9u[Qq]
[c]ZGlveGlkZQ==[Qq]
[q]In the diagram below, the acronym for compound “f” is [hangman], and the acronym for compound “d” is [hangman].
[c]UnVCUA==[Qq]
[c]RzNQ[Qq]
[q]In the diagram below, Phase I is [hangman] [hangman], and phase II is [hangman] [hangman].
[c]Y2FyYm9u[Qq]
[c]Zml4YXRpb24=[Qq]
[c]ZW5lcmd5[Qq]
[c]aW52ZXN0bWVudA==[Qq]
[x][restart]
[/qwiz]
What’s Next?
This tutorial completes AP Bio Unit 3 (Cellular Energetics).
- To review all of Unit 3 (Cellular Energetics), please go to our Unit 3 Review Page: Objectives, Flashcards, and Quizzes
- To choose another tutorial in our AP Bio Video Pathway, go to the AP Bio Video Pathway Main Menu
- To prepare for the AP Bio Exam, go to our AP Bio Review Menu to access flashcards, MCQs, FRQs, and Click-On Challenge games.
