Looking for a student learning guide? It’s on the main menu for your course. Use the “Courses” menu above.
1. Steroid hormones (like testosterone and estrogen) regulate gene expression
In the previous tutorials in this unit, our discussion of hormones and signaling pathways focused on activating dormant enzymes in the cytoplasm. This allows for quick responses, such as quickly breaking down glycogen into glucose for the fight-or-flight response. These responses are a key component of homeostasis: the dynamic maintenance of optimal internal conditions, despite changes in the external environment.
Now we’ll turn to steroid hormones, which have longer-term effects on cells and organisms. These effects involve the regulation of genes, switching them on and off, which changes the proteins a cell produces. Just think, for a moment, about the effect steroid hormones like testosterone and estrogen had on your body when you went through puberty. These hormones brought about long-term changes in your body’s form (everything from an Adam’s apple in males to breasts in females) and function (sexual maturation in both sexes, the start of ovulation and menstruation in females).
How do steroid hormones work to activate genes? Let’s take a look at two of the most well-known steroid hormones.
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-testosterone and estrogen (M11)”]
[h]Testosterone and estrogen
[i]
| Estrogen |
Testosterone |
[q]How would you classify these hormones?
| Estrogen |
Testosterone |
[c]Y2FyYm9oeWRyYXRl[Qq]
[f]Tm86IGNhcmJvaHlkcmF0ZXMgYXJlIHBvbHltZXJzIG9mIG1vbm9zYWNjaGFyaWRlcyAoc2ltcGxlIHN1Z2FycykuIE5vIHN1Z2FycyBhcmUgc2hvd24gYWJvdmUu[Qq]
[c]bGlw aWQ=[Qq]
[f]RXhjZWxsZW50OiBlc3Ryb2dlbiBhbmQgdGVzdG9zdGVyb25lIGFyZSBsaXBpZHMu[Qq]
[c]cHJvdGVpbg==[Qq]
[f]Tm86IHByb3RlaW5zIGFyZSBwb2x5bWVycyBvZiBhbWlubyBhY2lkcywgYW5kIGhhdmUgdmVyeSBjb21wbGV4IHRocmVlLWRpbWVuc2lvbmFsIHNoYXBlcy4gTWFrZSBhbm90aGVyIGNob2ljZSBuZXh0IHRpbWUu[Qq]
[c]bnVjbGVpYyBhY2lk[Qq]
[f]Tm86IG51Y2xlaWMgYWNpZHMgYXJlIHBvbHltZXJzIG9mIG51Y2xlb3RpZGVzLiBNYWtlIGFub3RoZXIgY2hvaWNlIG5leHQgdGltZS4=[Qq]
[q]In terms of their interaction with water, molecules like estrogen and testosterone are
| Estrogen |
Testosterone |
[c]SHlkcm9w aG9iaWM=[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBEZXNwaXRlIHRoZSBoeWRyb3h5bCBncm91cHMsIHRoZSBiaWcgZnVzZWQgY2FyYm9uIHJpbmdzIHNob3duIGFib3ZlIGFyZSBnb2luZyB0byBtYWtlIHRoaXMgbW9sZWN1bGUgbm9uLXBvbGFyLCBhbmQgdGhlcmVmb3JlIGh5ZHJvcGhvYmljLg==[Qq]
[c]SHlkcm9waGlsaWMu[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIE5vdGljZSB0aGUgZm91ciBmdXNlZCBjYXJib24gcmluZ3MgdGhhdCBtYWtlIHVwIHRoZSBidWxrIG9mIHRoZXNlIG1vbGVjdWxlcy4gSG93IGRvIHlvdSB0aGluayB0aGVzZSByaW5ncyBhcmUgZ29pbmcgdG8gaW50ZXJhY3Qgd2l0aCB3YXRlcj8=[Qq]
[x]Note that steroid hormones are lipids, and they’re hydrophobic. That sets up the way they’ll interact with cells and cell membranes, which you’ll learn about below.
[/qwiz]
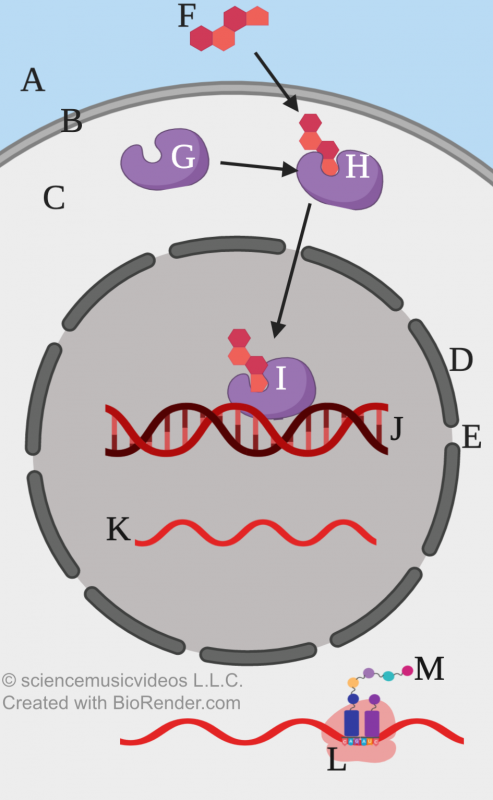
A general scheme for steroid hormone action is shown on the right. The first thing to note is that because steroid hormones (“F”) are lipids (and therefore non-polar and hydrophobic), they can pass right through the cell’s phospholipid bilayer (“B”) and diffuse into the cytoplasm (“C”).
Floating in the cytoplasm of the cells that are the targets for a steroid hormone are mobile receptors (“G”). The hormone binds with the receptor forming a receptor-hormone complex (“H”). This complex can pass through the nuclear membrane (“D”) at a nuclear pore (“E”), where it binds with DNA (“J”) and acts as a transcription factor (“I”).
Transcription factors cause genes to be expressed. That involves the production of messenger RNA (“K”). The RNA diffuses out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm. There, the messenger RNA is read by a ribosome (“L”) and then transcribed into protein (“M”).
To connect this back to puberty, protein production is what the changes in your body’s form and function were all about. Protein is the tissue that makes up the increased muscle mass that you gained if you’re a male. Protein is what makes up the skin and underlying structure of breast tissue if you’re female.
2. Some Water-Soluble Hormones have Signal Transduction Pathways that Regulate Genes
While steroid hormones are typically associated with gene regulation, there are some water-soluble (polar) hormones that also work through regulating genes.
One example of this is growth hormone, which is secreted by the pituitary gland, in the brain. As its name indicates, growth hormone stimulates cell reproduction and plays a key role in animal development. Click here to read more about growth hormones on Wikipedia.
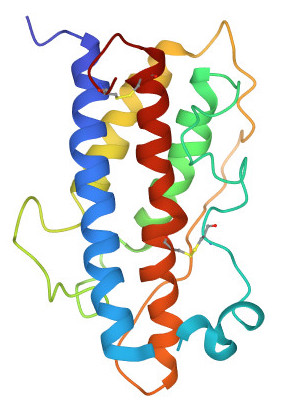
You can see a cartoon version of growth hormone’s structure on your right. Each alpha helix is composed of dozens of amino acids. The entire molecule is composed of 191 amino acids, making growth hormone much too big and polar to pass through the phospholipid bilayer. Consequently, it works through a mechanism that’s similar to what’s shown below (though the actual metabolic pathway associated with growth hormone is much more complicated).
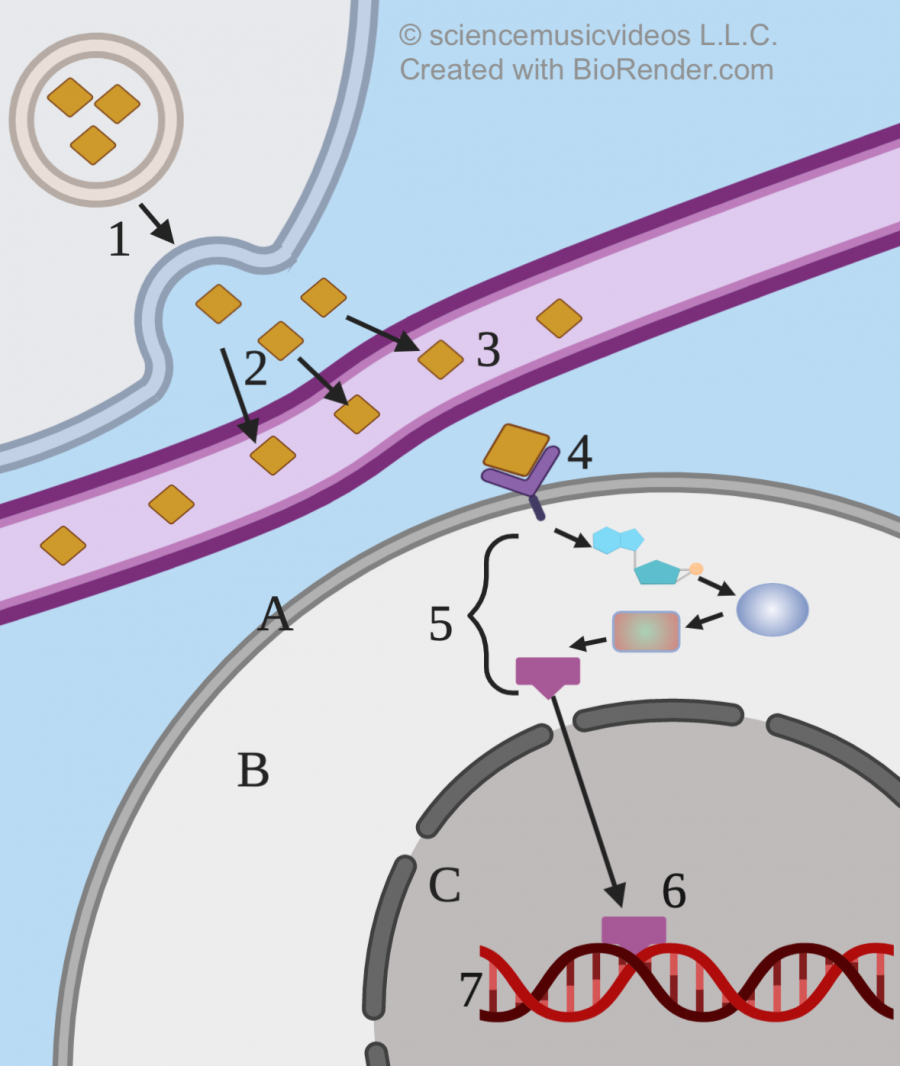 The process starts with the hormone being released from a vesicle in a cell of a hormone-producing gland (“1”). The hormone diffuses from the extracellular space into the bloodstream (“2”) and then circulates throughout the body, diffusing out of the bloodstream (“3”) and binding with target cells that have a complementary membrane receptor (“4”). After binding with the receptor, the message needs to be transduced through a signal transduction pathway (“5”) in the cytoplasm (“B”). The last molecule in this pathway (“6”) diffuses into the nucleus (“C”) through a nuclear pore, and then interacts with the cell’s DNA (“7”), either activating or deactivating genes.
The process starts with the hormone being released from a vesicle in a cell of a hormone-producing gland (“1”). The hormone diffuses from the extracellular space into the bloodstream (“2”) and then circulates throughout the body, diffusing out of the bloodstream (“3”) and binding with target cells that have a complementary membrane receptor (“4”). After binding with the receptor, the message needs to be transduced through a signal transduction pathway (“5”) in the cytoplasm (“B”). The last molecule in this pathway (“6”) diffuses into the nucleus (“C”) through a nuclear pore, and then interacts with the cell’s DNA (“7”), either activating or deactivating genes.
3. Quiz: Hormones and Gene Regulation
[qwiz random=”true” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Hormones and Gene Regulation (M11)” style=”width: 550px !important; min-height: 400px !important;”]
[h] Hormones and Gene Regulation
[i]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|6229b971a1fff” question_number=”1″] In the diagram below, which letter represents the cell membrane?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE I=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcQuKAnSByZXByZXNlbnRzIHRoZSBtZW1icmFuZS4=[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBUaGUgc2lnbmFsIGNvbWVzIGZyb20gb3V0c2lkZSB0aGUgY2VsbCwgYW5kLCBpbiB0aGUgY2FzZSBvZiBhIHN0ZXJvaWQgaG9ybW9uZSwgZGlmZnVzZXMgdGhyb3VnaCB0aGUgbWVtYnJhbmUuIElmICYjODIyMDtBJiM4MjIxOyByZXByZXNlbnRzIHRoZSBjZWxsIGV4dGVyaW9yLCB3aGljaCBsZXR0ZXIgcmVwcmVzZW50cyB0aGUgbWVtYnJhbmU/
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|6223c21329bff” question_number=”2″] In the diagram below, which letter could represent a steroid hormone (such as testosterone or estrogen)?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE Y=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcRuKAnSByZXByZXNlbnRzIGEgc3Rlcm9pZCBob3Jtb25lLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBUaGUgc2lnbmFsIGNvbWVzIGZyb20gb3V0c2lkZSB0aGUgY2VsbCwgdGhlbiBkaWZmdXNlcyB0aHJvdWdoIHRoZSBtZW1icmFuZS4gSWYgJiM4MjIwO0EmIzgyMjE7IHJlcHJlc2VudHMgdGhlIGNlbGwgZXh0ZXJpb3IsIHdoaWNoIGxldHRlciBjb3VsZCByZXByZXNlbnQgdGhlIHNpZ25hbCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3MgYWJvdXQgdG8gZW50ZXIgdGhlIGNlbGw/
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCBuby4=[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|621e5fb7aa7ff” question_number=”3″] In the diagram below, which letter could represent a cytoplasmic receptor (before it binds with the signal)?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE c=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcR+KAnSByZXByZXNlbnRzIGEgY3l0b3BsYXNtaWMgcmVjZXB0b3Iu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBUaGUgc2lnbmFsIGNvbWVzIGZyb20gb3V0c2lkZSB0aGUgY2VsbCwgdGhlbiBkaWZmdXNlcyB0aHJvdWdoIHRoZSBtZW1icmFuZSwgdGhlbiBiaW5kcyB3aXRoIGEgY3l0b3BsYXNtaWMgcmVjZXB0b3IuIElmICYjODIyMDtGJiM4MjIxOyByZXByZXNlbnRzIHRoZSBzaWduYWwsIHRoZW4gd2hhdCBpbnNpZGUgdGhlIGNlbGwgY291bGQgcmVwcmVzZW50IGFuIGVtcHR5IHJlY2VwdG9yIHRoYXQgdGhlIHNpZ25hbCBjYW4gYmluZCB3aXRoPw==
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCBuby4=[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|6217d356393ff” question_number=”4″] In the diagram below, which letter shows a receptor/hormone complex interacting with DNA?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE k=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcSeKAnSBzaG93cyBhIHJlY2VwdG9yL2hvcm1vbmUgY29tcGxleCBpbnRlcmFjdGluZyB3aXRoIEROQS4=[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBUaGUgc2lnbmFsIGNvbWVzIGZyb20gb3V0c2lkZSB0aGUgY2VsbCwgdGhlbiBkaWZmdXNlcyB0aHJvdWdoIHRoZSBtZW1icmFuZSwgdGhlbiBiaW5kcyB3aXRoIGEgY3l0b3BsYXNtaWMgcmVjZXB0b3IsIHdoaWNoIHRoZW4gZGlmZnVzZXMgaW50byB0aGUgbnVjbGV1cyB3aGVyZSBpdCBpbnRlcmFjdHMgd2l0aCBETkEuIEZpbmQgRE5BIGluc2lkZSB0aGUgbnVjbGV1cywgZmlndXJlIG91dCB3aGF0IHRoZSByZWNlcHRvciBpcywgYW5kIHlvdSYjODIxNztsbCBoYXZlIHlvdXIgYW5zd2VyLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCBuby4=[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|6211b6b702bff” question_number=”5″] In the diagram below, which letter shows RNA that’s just been transcribed as a result of the hormone/receptor complex having interacted with the cell’s DNA?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE s=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcS+KAnSBzaG93cyBSTkEgdGhhdCYjODIxNztzIGp1c3QgYmVlbiB0cmFuc2NyaWJlZCBhcyBhIHJlc3VsdCBvZiB0aGUgaG9ybW9uZS9yZWNlcHRvciBjb21wbGV4IGhhdmluZyBpbnRlcmFjdGVkIHdpdGggdGhlIGNlbGwmIzgyMTc7cyBETkEu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiAmIzgyMjA7SCYjODIyMTsgc2hvd3MgYSByZWNlcHRvci9ob3Jtb25lIGNvbXBsZXggaW4gdGhlIGN5dG9wbGFzbS4gTm93LCBmaW5kIEROQSBpbiB0aGUgbnVjbGV1cy4gTm93LCBmaW5kIGEgc2luZ2xlLXN0cmFuZGVkIG1vbGVjdWxlIHRoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBiZWVuIHByb2R1Y2VkIGFzIGEgcmVzdWx0IG9mIHRoZSBpbnRlcmFjdGlvbiBiZXR3ZWVuIHRoZSByZWNlcHRvci9ob3Jtb25lIGNvbXBsZXggYW5kIEROQSwgYW5kIHlvdSYjODIxNztsbCBoYXZlIHlvdXIgYW5zd2VyLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|620c545b837ff” question_number=”6″] In the diagram below, which letter shows a nuclear pore?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE U=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcReKAnSBzaG93cyBhIG51Y2xlYXIgcG9yZS4=[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBOdWNsZWFyIHBvcmVzIGFyZSBwYXNzYWdld2F5cyBmb3IgbWF0ZXJpYWxzIHRvIGVudGVyIGFuZCBsZWF2ZSB0aGUgbnVjbGV1cy4gRmluZCB0aGUgbnVjbGVhciBtZW1icmFuZSwgYW5kIHRoZW4gbG9jYXRlIGEgbnVjbGVhciBwb3JlLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|6206a77e87bff” question_number=”7″] In the diagram below, which letter shows a ribosome?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE w=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcTOKAnSBzaG93cyBhIHJpYm9zb21lLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBSaWJvc29tZXMgdHJhbnNsYXRlIHRoZSBtZXNzYWdlcyBpbiBSTkEgaW50byBhIHByb3RlaW4sIGFuIGFjdGl2aXR5IHRoYXQgb2NjdXJzIGluIHRoZSBjeXRvcGxhc20uIElmICYjODIyMDtLJiM4MjIxOyBpcyBSTkEgaW4gdGhlIG51Y2xldXMsIHRoZW4gd2hhdCBsZXR0ZXIgY291bGQgaW5kaWNhdGUgYSByaWJvc29tZSB0cmFuc2xhdGluZyB0aGF0IFJOQSBpbnRvIHByb3RlaW4/
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|6200faa18bfff” question_number=”8″] In the diagram below, which letter shows a protein that’s produced as the cellular response to the steroid hormone signal?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE 0=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcTeKAnSBzaG93cyBhIHByb3RlaW4gdGhhdCYjODIxNztzIGJlaW5nIHN5bnRoZXNpemVkIGFzIGEgcmVzdWx0IG9mIHRoZSBob3Jtb25lIHNpZ25hbCB0aGF0IGRpZmZ1c2VkIGludG8gdGhlIGNlbGwsIHRoZW4gYm91bmQgd2l0aCBhIHJlY2VwdG9yIGFuZCBhY3RpdmF0ZWQgYSBnZW5lLCB1bHRpbWF0ZWx5IHJlc3VsdGluZyBpbiB0aGlzIHByb3RlaW4mIzgyMTc7cyB0cmFuc2xhdGlvbi4=[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBGb3Igc3Rlcm9pZCBob3Jtb25lcywgdGhlIGNlbGx1bGFyIHJlc3BvbnNlIGlzIHRoZSBwcm9kdWN0aW9uIG9mIGEgcHJvdGVpbi4gSWYgJiM4MjIwO0wmIzgyMjE7IHJlcHJlc2VudHMgYSByaWJvc29tZSwgdGhlIGNlbGwmIzgyMTc7cyBwcm90ZWluIGZhY3RvcnksIHRoZW4gd2hhdCBjb3VsZCByZXByZXNlbnQgYSBwcm90ZWluIHRoYXQgdGhpcyByaWJvc29tZSBpcyBzeW50aGVzaXppbmc/
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61fb98460cbff” question_number=”9″] In the diagram below, “I” represents [hangman].
[c]IHJlY2VwdGlvbg==[Qq]
[f]IFllcywgJiM4MjIwO0kmIzgyMjE7IHJlcHJlc2VudHMgcmVjZXB0aW9uLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61f5c62852bff” question_number=”10″] In the diagram below, “II” represents [hangman].
[c]IHRyYW5zZHVjdGlvbg==[Qq]
[f]IFllcywgJiM4MjIwO0kmIzgyMjE7IHJlcHJlc2VudHMgdHJhbnNkdWN0aW9uLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61f0194b56fff” question_number=”11″] In the diagram below, “III” (and “4”) represents a cellular [hangman].
[c]IHJlc3BvbnNl[Qq]
[f]IFllcywgJiM4MjIwO0lJSSYjODIyMTsgcmVwcmVzZW50cyB0aGUgY2VsbHVsYXIgcmVzcG9uc2Uu
Cg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61ea6c6e5b3ff” question_number=”12″] The diagram below shows a hormone that would be chemically classified as a [hangman].
[c]IHN0ZXJvaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IFllcywgVGhlIGRpYWdyYW0gaXMgc2hvd2luZyBob3cgYSBzdGVyb2lkIGhvcm1vbmUgYWZmZWN0cyBpdHMgdGFyZ2V0IGNlbGwu[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61e4e4d21dbff” question_number=”13″] In the diagram below, which number or letter shows a hormone in a vesicle in a hormone secreting cell?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID E=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcMeKAnSBzaG93cyBhIGhvcm1vbmUgaW4gYSB2ZXNpY2xlIGluIGEgaG9ybW9uZS1zZWNyZXRpbmcgY2VsbC4=[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBWZXNpY2xlcyBhcmUgbWVtYnJhbmUtZW5jbG9zZWQgYnViYmxlcyB0aGF0IG9mdGVuIGNvbnRhaW4gYSBzdWJzdGFuY2UgdGhhdCBhIGNlbGwgaXMgYWJvdXQgdG8gZXhwb3J0LiBXaGljaCBudW1iZXIgaXMgbmVhciBzb21ldGhpbmcgdGhhdCBjb3VsZCBmaXQgdGhhdCBkZXNjcmlwdGlvbj8=[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61df12b463bff” question_number=”14″] In the diagram below, which number or letter shows a signal transduction pathway?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID U=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcNeKAnSBzaG93cyBhIHNpZ25hbCB0cmFuc2R1Y3Rpb24gcGF0aHdheS4=[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBUaGUgc2lnbmFsIHRyYW5zZHVjdGlvbiBwYXRod2F5IG9jY3VycyBpbiB0aGUgY3l0b3BsYXNtLCB3aGljaCBpcyByZWdpb24gJiM4MjIwO2IuJiM4MjIxOyBJbiB0aGlzIGNhc2UsIHRoZSBwYXRod2F5IGlzIHRha2luZyBhIG1lc3NhZ2UgZnJvbSB0aGUgbWVtYnJhbmUgaW50byB0aGUgbnVjbGV1cy4=[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCBuby4=[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61d65787ccbff” question_number=”15″] What number or letter below shows a molecule from a signaling pathway interacting with DNA?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID Y=[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4g4oCcNuKAnSBzaG93cyBhIHByb3RlaW4ga2luYXNlIGludGVyYWN0aW5nIHdpdGggRE5BLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBETkEgaXMgaW5zaWRlIHRoZSBudWNsZXVzLCB3aGljaCBpcyByZWdpb24gJiM4MjIwO2MuJiM4MjIxOw==[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIGxldHRlcg==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61d0f52c4d7ff” question_number=”16″] Because of the way the hormone is binding with a membrane receptor, we can conclude that it must be [hangman].
[c]IHBvbGFy[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61ca8e0b9a7ff” question_number=”17″] Number “5” below is a signal [hangman] pathway.
[c]IHRyYW5zZHVjdGlvbg==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_Hormones and Gene Regulation (cell communication)|61c1d2df037ff” question_number=”18″] The diagram below shows how a hormone circulates everywhere in the body, but only has an effect in [hangman] cells.
[c]IHRhcmdldA==[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[x][restart]
[/qwiz]
Next Steps
This tutorial ends this series of tutorials about cell signaling.
- To pull it all together, take this comprehensive quiz about everything you’ve learned in this module. Then write up a summary in your student learning guide.
- Return to the Cell Communication Main Menu