Looking for a student learning guide? It’s linked in the main menu for your course. Use the “Courses” menu above.
1. “Nothing in Biology Makes Sense Except in the Light of Evolution”
Evolution is the idea that life changes over time. You can think of this in terms of looking back to the past, and into the future.
- Looking backward: the animals, plants, and other organisms around you are the modified descendants of their ancestors that lived in the past.
- Looking forward: these same organisms are members of populations that will either continue to evolve into the future or, like the vast majority of the species that have ever lived, become extinct.
Evolution’s importance to biology was memorably stated by biologist Theodosius Dobzhansky who wrote that “Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution.”
What’s the evidence that evolution is true?
In what follows below and in the next three tutorials, we’ll look at the evidence supporting evolution. Because evolution is a scientific theory, let’s start by clarifying what a theory is, and how the word theory is used in a scientific context.
2. A theory is much more than a hypothesis
In common speech, the word theory is often used in a way that’s synonymous with the word “opinion” or “belief.” For example, you’ve probably heard someone say something like: “That’s your theory. Let me tell you mine.”
That use of the word theory is closer to the scientific idea of a hypothesis. A hypothesis is an idea that requires testing. In science, a theory is an explanation that’s already been tested many times. Unlike a hypothesis, a theory is supported by a significant amount of evidence.
To sharpen your ability to distinguish between a scientific theory and a hypothesis, read the following passages.
A theory explains a phenomenon, accounts for all available data, is supported by a huge body of evidence. Hypotheses are just guesses that need testing.
Adapted from: Ruth Levy Guyer, Professor of Immunology and Bioethics, Johns Hopkins University and Haverford College.
A theory is a well-established principle that has been developed to explain some aspect of the natural world…while a hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a specified set of circumstances. A theory has been extensively tested and is generally accepted…A hypothesis is a speculative guess that has yet to be tested.
Adapted from Kendra Cherry, About.com, Introduction to Research Methods
So, before we look at the evidence for the theory of evolution, let’s make sure that the distinction between theory and hypothesis is clear.
[qwiz style = “border: 3px solid black; ” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Evidence for evo: theory v. hypothesis”]
[h]Theory v. Hypothesis
[i]Biohaiku
Theory in science
A validated idea
Much more than a hunch
[q]In the scientific method, the next step after posing an initial question or making an interesting observation is to formulate a testable
[c]aHlwb3Ro ZXNpcy4=[Qq]
[c]dGhlb3J5Lg==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBBIGh5cG90aGVzaXMgaXMgYSB0ZXN0YWJsZSBpZGVhLg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoZW9yaWVzIGFyZSBNVUNIIGJpZ2dlciB0aGFuIHRlc3RhYmxlIGlkZWFzLiBUaGVvcmllcyBzdGFuZCBvbiBhIHNvbGlkIGZvdW5kYXRpb24gb2YgYWNjdW11bGF0ZWQgZXZpZGVuY2Uu
Cg==[Qq]
[q]In the 1800s, two German scientists proposed that all living things are composed of cells, and that cells are the fundamental units of life. During the past two hundred years, no living thing has ever been discovered that does not consist of cells. At this point, these ideas about cells are best understood as being a
[c]aHlwb3RoZXNpcy4=[Qq]
[c]dGhlb3 J5Lg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoaXMgaWRlYSwgd2hpY2ggYXBwbGllcyB0byBhbGwgbGlmZSwgaXMgbXVjaCBiaWdnZXIgdGhhbiBhIGh5cG90aGVzaXMu[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBUaGlzIGlzIHRoZSBjZWxsIHRoZW9yeS4gSXQgaGFzIGVub3Jtb3VzIHByZWRpY3RpdmUgcG93ZXIsIGFuZCBoYXMgYmVlbiBjb25maXJtZWQgYnkgZXZlcnkgbGl2aW5nIHRoaW5nIGV2ZXIgZGlzY292ZXJlZC4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A specific and testable proposal that attempts to explain a limited set of phenomena is a
[c]aHlwb3Ro ZXNpcy4=[Qq]
[c]dGhlb3J5Lg==[Qq]
[f]Q29ycmVjdDrCoEEgc3BlY2lmaWMgYW5kIHRlc3RhYmxlIHByb3Bvc2FsIHRoYXQgYXR0ZW1wdHMgdG8gZXhwbGFpbiBhIGxpbWl0ZWQgc2V0IG9mIHBoZW5vbWVuYSBpcyBhwqA=aHlwb3RoZXNpcy4=[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEEgdGhlb3J5IGlzIGEgd2VsbCBlc3RhYmxpc2hlZCBwcmluY2lwbGUuIFdoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyBkZXNjcmliZWQgYWJvdmUgaXMgbXVjaCB0b28gbmFycm93IHRvIGJlIGEgdGhlb3J5Lg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Scientists are measuring the effect of a certain hormone on the growth of breast cancer cells. They think that this hormone might increase the growth of tumors. This is an example of a
[c]aHlwb3Ro ZXNpcy4=[Qq]
[c]dGhlb3J5Lg==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBBIHNwZWNpZmljLCBsaW1pdGVkIHByZWRpY3Rpb24gc3VjaCBhcyB0aGUgb25lIGxpc3RlZCBhYm92ZSBpcyBhIHBlcmZlY3QgZXhhbXBsZSBvZiBhIGh5cG90aGVzaXMu[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoaXMgaXMgbXVjaCB0b28gbGltaXRlZCBhbiBpZGVhIHRvIHF1YWxpZnkgYXMgYSB0aGVvcnkuIFRoZW9yaWVzIGFyZSBiaWcuIFRoZXkgZXhwbGFpbiBhIGxvdCBvZiB0aGluZ3MuIFRoaW5rIG9mIGdyYXZpdHkgb3IgZXZvbHV0aW9uIHRvIHJlbWluZCB5b3Vyc2VsZiBhYm91dCB0aGUgZW5vcm1vdXMgc2NvcGUgb2YgYSB0aGVvcnku
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A proposed idea about the speed of falling objects was published by a scientist in the 1600s. Over the next centuries, this proposal was supported by a variety of experiments on Earth, and by observations of objects in space. No observation refuting this idea has ever been made. At this point, this idea is best classified as a
[c]aHlwb3RoZXNpcy4=[Qq]
[c]dGhlb3 J5Lg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoaXMgaXMgbXVjaCB0b28gZ3JhbmQgdG8gYmUgYSBoeXBvdGhlc2lzLiBJdCBjb3ZlcnMgZmFsbGluZyBvYmplY3RzLCBhbmQgb2JqZWN0cyBpbiBzcGFjZS4gQSBoeXBvdGhlc2lzIHdvdWxkIGJlIG11Y2ggbW9yZSBuYXJyb3csIGFuZCBub3QgZXhwbGFpbiBzdWNoIGEgd2lkZSB2YXJpZXR5IG9mIHRoaW5ncy4=[Qq]
[f]WWVzOiB0aGlzIGlzIHRoZSB0aGVvcnkgb2YgZ3Jhdml0eS4gSXQgaGFzIGVub3Jtb3VzIHBvd2VyIHRvIGV4cGxhaW4sIGFuZCBpdCYjODIxNztzIGJlZW4gcmVwZWF0ZWRseSBjb25maXJtZWQgZm9yIGh1bmRyZWRzIG9mIHllYXJzLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world, based on a body of facts that have been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experiment.
[c]aHlwb3RoZXNpcy4=[Qq]
[c]dGhlb3 J5Lg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEEgaHlwb3RoZXNpcyBpcyBhIHRlbnRhdGl2ZSBwcmVkaWN0aW9uIHRoYXQgc3RpbGwgbmVlZHMgdG8gYmUgY29uZmlybWVkIGJ5IGV4cGVyaW1lbnQu[Qq]
[f]WWVzLsKgQSB3ZWxsLXN1YnN0YW50aWF0ZWQgZXhwbGFuYXRpb24gb2Ygc29tZSBhc3BlY3Qgb2YgdGhlIG5hdHVyYWwgd29ybGQsIGJhc2VkIG9uIGEgYm9keSBvZiBmYWN0cyB0aGF0IGhhdmUgYmVlbiByZXBlYXRlZGx5IGNvbmZpcm1lZCB0aHJvdWdoIG9ic2VydmF0aW9uIGFuZCBleHBlcmltZW50wqA=aXMgYSBiZWF1dGlmdWwgZGVmaW5pdGlvbiBvZiBhIHRoZW9yeS4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]A group of students sets up an experiment to test the idea that tomato plants grown in blue light will produce larger fruit than tomatoes grown in regular sunlight. This idea would best be classified as a
[c]aHlwb3Ro ZXNpcy4=[Qq]
[c]dGhlb3J5Lg==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBUaGUgbmFycm93bmVzcyBvZiB0aGUgaWRlYSBhbmQgaXRzIHRlbnRhdGl2ZSBuYXR1cmUgY2xhc3NpZnkgdGhpcyBhcyBhIGh5cG90aGVzaXMu[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEEgdGhlb3J5IHdvdWxkIGhhdmUgdG8gYmUgbXVjaCB3aWRlciBpbiBzY29wZSwgYW5kIG11Y2ggbW9yZSBwb3dlcmZ1bCBpbiBpdHMgYWJpbGl0eSB0byBleHBsYWluIHRoaW5ncy4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]The idea that all infectious diseases are caused by germs (bacteria or viruses) has been repeatedly confirmed by hundreds of observations. This idea is a
[c]aHlwb3RoZXNpcy4=[Qq]
[c]dGhlb3 J5Lg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoaXMgaXMgYW4gaWRlYSB0aGF0IGNvdmVycyBBTEwgaW5mZWN0aW91cyBkaXNlYXNlcy4gSXQmIzgyMTc7cyBtdWNoIHRvbyBicm9hZCB0byBiZSBhIGh5cG90aGVzaXMu[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBUaGlzIGlzIHRoZSBnZXJtIHRoZW9yeSBvZiBkaXNlYXNlLCBhbmQgaXQmIzgyMTc7cyBiZWVuIHJlcGVhdGVkbHkgY29uZmlybWVkIGZvciB0aGUgcGFzdCAxNTAgeWVhcnMu[Qq]
[x]
If you want to take this quiz again, click the button below
[restart]
[/qwiz]
3. To prove evolution true, we need evidence of descent with modification
When Darwin talked about the process of evolution, he used the term descent with modification. Descent with modification means that as a population produces descendants, these descendants might evolve in ways that make them different from their current form. Or, if you run the clock backwards, it means that the current form of a population (or an entire species) might be different from its ancestral form.

Let’s think about this in terms of a familiar animal: the dog. Based on archeological and genetic evidence, we know that dogs are domesticated wolves. If you could look back 10,000 years, the ancestors of dogs would be different from the dogs you see today. That’s because 10,000 years ago, the process of domestication of dogs was just beginning. People had dogs, but many of the breeds we know today (like poodles or dachshunds) didn’t exist. If you went back 100,000 years there wouldn’t be any dogs at all: just wolves. If you went back 100,000,000 years, there wouldn’t be wolves, but rather an ancient, earlier mammalian species that was in the line that, millions of years later, led to wolves.
So if we want to prove that evolution has happened, we need to find evidence of descent with modification. We can find this in two ways.
- We can look for changes in a population’s phenotype over time. Through studying fossils and comparing the anatomy of existing organisms, scientists have been gathering this type of evidence since the start of the 1800s (even before Darwin and Wallace formulated their idea of natural selection).
- We can look for changes in a population’s genotype. As we saw in the last module, evolution is about changes in the allele frequencies in a population’s gene pool. So, by comparing the genes of existing organisms, we should be able to see evidence of mutations emerging, and alleles rising and falling in frequency.

As we consider this evidence, we’re going to look for two patterns. We can track these in the image to the left, a sketch by Darwin in one of his notebooks. Darwin made this sketch in 1837 (twenty two years before his publication of The Origin of Species), and it’s thought to represent his “Eureka” moment (when he first figured out the pattern of evolution).
The first pattern is change in a single lineage, over time. A lineage is a line of descent that links ancestors and descendants. If “1” at left represents an ancestral species, then A, B, C, and D are all descendant species. If you follow the line from 1 to any of its descendants, you should be able to observe descent with modification along the way.
The second way that evolution unfolds is shown by the diagram’s branching pattern. Since species 1 is the ancestral species that gave rise to A, B, C, and D, then all of these descendant species should have shared features that result from their common ancestry. If this diagram were of a family, then A, B, C and D would be cousins.
Flipping that logic gives us a way to find evidence of evolution. Pretend this is a family tree. If you didn’t know that B and C were related, but you did a DNA test and and found that they shared a certain percentage of their genes, you would have to conclude that they were related: siblings, cousins, etc. And while it’s less direct, if you found certain shared inherited phenotypes, that would lead you to the same conclusion.
With species, you can do the same thing. Shared DNA sequences can serve as evidence of common descent. So can shared inherited phenotypes. After all, if these species weren’t the descendants of a common ancestor, why would they share DNA sequences, or other inherited traits?
So, to prove evolution true, we’re looking for evidence of descent with modification. We can look for that in
- Changes in phenotypes within a lineage of organisms
- Genetic change in a population’s gene pool.
- Shared inherited structures, molecules, or gene sequences that confirm life’s branching pattern.
4. Observations of Evolution in Recent Times
When Darwin first formulated his theory of evolution by natural selection, he saw change in the natural world as something that would occur very slowly. Hence, his view of evolution was one in which changes would be imperceptibly slow, over hundreds of thousands or millions of years, and only discernible in hindsight.
However, a variety of studies during the late 19th, 20th, and 21st century have shown that evolution can proceed rapidly. In other words, scientists have observed both descent with modification, and changes in a population’s genetic structure. Here are a few examples.
4a. Evolution of Antibiotic resistant bacteria and the rise of MRSA.
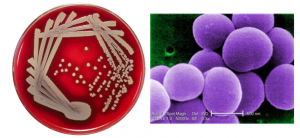
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium. It’s one of many bacterial species that usually live harmlessly on our skin and other parts of our bodies. But there are also pathogenic forms that can cause skin and sinus infections, along with food poisoning, pneumonia, and wound infections. Up to 50,000 deaths/year are associated with S. aureus infections, and about 500,000 hospital patients become infected with S. aureus each year.
Bacterial infections by S. aureus can be treated with antibiotics: substances that kill bacteria or inhibit bacterial growth. However, widespread use of antibiotics has created selective pressure for S. aureus (and other infectious bacteria) to evolve antibiotic resistance, making antibiotics increasingly ineffective. The first widely used antibiotic, penicillin, was introduced in 1943. By the 1950s, penicillin-resistant strains of S. aureus were common.
Natural selection was at work. S. aureus populations have genetic variation. Most bacterial cells can’t reproduce when exposed to penicillin, a molecule that inhibits bacterial cell wall formation. But some bacterial cells produce an enzyme called penicillinase, which breaks apart penicillin, making it ineffective. These individual bacterial cells were able to survive the doses of penicillin that killed off the rest of the population. When the survivors reproduced, they passed along their genes for resistance. By 1950, only seven years after penicillin was introduced, 40% of S. aureus studied were penicillin-resistant. By 1960, this had risen to 80%. Now it’s about 98%.
Some other features of bacterial reproduction have enhanced the spread of resistance. Bacteria don’t only pass their genes on to their descendants. Through tiny, transferrable circles of DNA called plasmids, bacteria can also pass genes to other members of their population. This is called horizontal gene transfer. Transfer of antibiotic resistance genes through plasmids has further increased antibiotic resistance.
Here’s an infographic that illustrates the process.
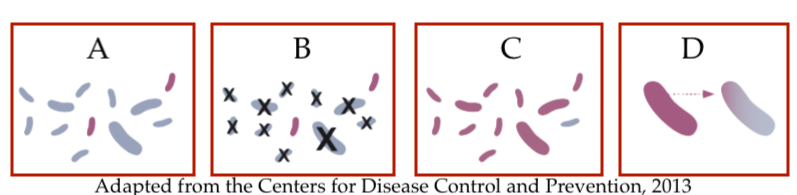
- Image “A shows the initial population. Most bacterial cells (the gray ones) are killed by the antibiotic. A small percentage are antibiotic-resistant. Note that the resistance is a pre-adaptation. It didn’t arise in response to the selective pressure, but was part of the population’s pre-existing genetic variation.
- Application of the antibiotic kills all the bacteria that are susceptible, leaving only those that are resistant.
- As the bacteria reproduce, the new population will be mostly composed of antibiotic-resistant cells.
- Horizontal gene transfer of genes for antibiotic resistance increases the proportion of antibiotic resistant individuals in the population.
Widespread use of antibiotics in agriculture has made the problem worse.
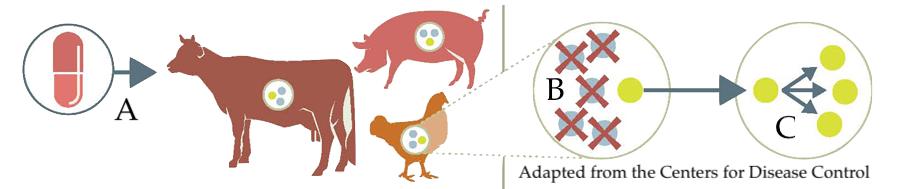
In agriculture, antibiotics are used to prevent outbreaks of infection in animals that are kept in close confinement. In 2013, the US Department of Agriculture estimated that 32 million pounds of antibiotics were used in food animal production. Another way to think of that amount is that 80% of the antibiotics used in the United States are used to raise animals (not to treat people with infections).
As with humans, the antibiotics fed to animals (A) kill only the susceptible bacteria. That selects antibiotic resistant strains (B and C). These can be transferred to people through animal products (contaminated meat), through produce (often lettuce) that’s been in contact with animal feces-contaminated soil or water, or during food preparation (which is why hand-washing is so important).
Methicillin is an antibiotic that was introduced in 1959. Like penicillin, methicillin inhibits bacterial cell wall formation, but through a different mechanism than penicillin. However, within two years of its introduction, methicillin-resistant bacteria had been observed. In this case, the resistant bacteria were able to use an enzyme to synthesize their cell walls through a mechanism that wasn’t inhibited by methicillin.
These methicillin-resistant bacteria have come to be known by the acronym MRSA (methicillin resistant S.aureus), and they’re much more dangerous than non-MRSA S. aureus. Often, MRSA infections can be controlled by other antibiotics, such as vancomycin. But the concern is that our arsenal of effective antibiotics is growing increasingly thin, as the bacteria mutate around whatever selective pressure our use of antibiotics creates.
Is this evidence for evolution? Absolutely. In the rise of antibiotic resistant bacteria, we have a clear example of descent with modification.
4b. Evolution of Pesticide Resistance in Mosquitoes

Mosquitoes are the primary way that the Plasmodium parasite that causes malaria spreads. Malaria is the number 1 killer of children worldwide, and killed 445,000 people in 2016, over half of whom were under the age of 5. The disease is particularly prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa (source: Forgotten Children Worldwide)
One approach to controlling malaria has been to suppress mosquito populations with insecticides (insect-killing chemicals). One such pesticide is DDT (dichlorophenyl trichloroethane). DDT was developed in the 1940s, and works by opening sodium channels in the membranes of insect nerve cells, causing these cells to misfire, leading to spasms and death.
Based on the story of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, you should be able to predict what happened.
Here’s a graph showing what happened when scientists measured the resistance of mosquitoes to exposure of 4% DDT solution for one hour. Measurements were done under controlled conditions, over a period of 18 months. Study the graph and answer the questions that follow. The term “mortality” on the Y axis means “certainty of death.”
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Evidence for evo: DDT”]
[h] DDT Resistance In Mosquitoes
[q] At which time period (A, B, or C) did the vast majority of the mosquitoes have pesticide resistance?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE M=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gQXQgcG9pbnQgJiM4MjIwO0MsJiM4MjIxOyBvbmx5IDIwJSBvZiB0aGUgbW9zcXVpdG9lcyBhcmUgZHlpbmcgYWZ0ZXIgMSBob3VyIG9mIGV4cG9zdXJlIHRvIHRoZSBzb2x1dGlvbi4gSWYgdGhleSYjODIxNztyZSBub3QgZHlpbmcsIHRoZXkgbXVzdCBiZSByZXNpc3RhbnQu[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IFNvcnJ5LCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBGaW5kIHRoZSBwb2ludCBpbiB0aW1lIHdoZW4gdGhlIG1vcnRhbGl0eSAodGhlIGFtb3VudCBvZiBkZWF0aCkgaXMgdmVyeSBsb3cuIFRoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyB3aGVuIG1vc3Qgb2YgdGhlIHBvcHVsYXRpb24gaXMgcmVzaXN0YW50Lg==[Qq]
[q] At which time period (A, B, or C) were the majority of the mosquitoes killed by DDT?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IE E=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gQXQgcG9pbnQgJiM4MjIwO0EsJiM4MjIxOyB0aGUgbW9ydGFsaXR5IGlzIGFsbW9zdCAxMDAlLiBUaGF0IG1lYW5zIHRoYXQgYXQgdGhpcyBwb2ludCBpbiB0aW1lLCB0aGUgbW9zcXVpdG9lcyBhcmUgc3VzY2VwdGlibGUgdG8gdGhlIEREVC4=[Qq]
[c]IEVudGVyIHdvcmQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLCB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGNvcnJlY3Qu[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBGaW5kIHRoZSBwb2ludCBpbiB0aW1lIHdoZW4gdGhlIG1vcnRhbGl0eSAodGhlIGFtb3VudCBvZiBkZWF0aCkgaXMgdmVyeSBoaWdoLiBUaGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgd2hlbiBtb3N0IG9mIHRoZSBwb3B1bGF0aW9uIGlzIHN0aWxsIHN1c2NlcHRpYmxlIHRvIEREVC4=[Qq]
[q] At point “C” in the graph below, most of the mosquitoes were [hangman] to DDT.
[c]IHJlc2lzdGFudA==[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[q multiple_choice=”true”] True or false: In response to DDT, mosquitoes developed a mutation that made them resistant.
[c]IHRydWU=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBOYXR1cmFsIHNlbGVjdGlvbiBpcyBub3QgYWJvdXQgcG9wdWxhdGlvbnMgcHJvZHVjaW5nIG11dGF0aW9ucyB0aGF0IGhlbHAgdGhlbSBzdXJ2aXZlIGVudmlyb25tZW50YWwgY2hhbGxlbmdlcy4gSXQmIzgyMTc7cyBhYm91dCB0aGUgZW52aXJvbm1lbnQgc2VsZWN0aW5nIHZhcmlhbnQgcGhlbm90eXBlcyB0aGF0IG1ha2UgdGhlIGluZGl2aWR1YWxzIHdobyBoYXZlIHRoZW0gbW9yZSBzdWl0ZWQgdG8gc3Vydml2aW5nIGFuZCByZXByb2R1Y2luZy4gVGhlIG11dGF0aW9uIHByZWNlZGVzIHRoZSBjaGFsbGVuZ2Uu[Qq]
[c]IGZh bHNl[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gTmF0dXJhbCBzZWxlY3Rpb24gaXMgbm90IGFib3V0IHBvcHVsYXRpb25zIHByb2R1Y2luZyBtdXRhdGlvbnMgdGhhdCBoZWxwIHRoZW0gc3Vydml2ZSBlbnZpcm9ubWVudGFsIGNoYWxsZW5nZXMuIEl0JiM4MjE3O3MgYWJvdXQgdGhlIGVudmlyb25tZW50IHNlbGVjdGluZyB2YXJpYW50IHBoZW5vdHlwZXMgdGhhdCBtYWtlIHRoZSBpbmRpdmlkdWFscyB3aG8gaGF2ZSB0aGVtIG1vcmUgc3VpdGVkIHRvIHN1cnZpdmluZyBhbmQgcmVwcm9kdWNpbmcuIFRoZSBtdXRhdGlvbiBwcmVjZWRlcyB0aGUgY2hhbGxlbmdlLg==[Qq]
[q multiple_choice=”true”] At which point in the graph below are there individuals with mutations that enable them to survive exposure to DDT?
[c]IEE=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBJdCYjODIxNztzIHRydWUgdGhhdCBzb21lIGluZGl2aWR1YWxzIGluIEEgbXVzdCBoYXZlIGhhZCBhIG11dGF0aW9uIHRoYXQgZW5hYmxlZCB0aGVtIHRvIHN1cnZpdmUgZXhwb3N1cmUgdG8gRERULiBCdXQgdGhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGJldHRlciBhbnN3ZXIu[Qq]
[c]IEI=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBJdCYjODIxNztzIHRydWUgdGhhdCBhYm91dCA1MCUgb2YgdGhlIGluZGl2aWR1YWxzIGluIEIgbXVzdCBoYXZlIGhhZCBhIG11dGF0aW9uIHRoYXQgZW5hYmxlZCB0aGVtIHRvIHN1cnZpdmUgZXhwb3N1cmUgdG8gRERULiBCdXQgdGhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGJldHRlciBhbnN3ZXIu[Qq]
[c]IEM=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBJdCYjODIxNztzIHRydWUgdGhhdCBtb3N0IGluZGl2aWR1YWxzIGluIEMgbXVzdCBoYXZlIGhhZCBhIG11dGF0aW9uIHRoYXQgZW5hYmxlZCB0aGVtIHRvIHN1cnZpdmUgZXhwb3N1cmUgdG8gRERULiBCdXQgdGhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGJldHRlciBhbnN3ZXIu[Qq]
[c]IEEsIEIs IGFuZCBD[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4gQWxsIG9mIHRoZXNlIHBvcHVsYXRpb25zIG11c3QgaGF2ZSBwb3NzZXNzZWQgaW5kaXZpZHVhbHMgd2l0aCBtdXRhbnQgcGhlbm90eXBlcyB0aGF0IGFsbG93ZWQgdGhlbSB0byBzdXJ2aXZlIGV4cG9zdXJlIHRvIEREVC4=[Qq]
[/qwiz]
4c. Evolution of new phenotypes in response to host changes in the Soapberry bug

The soapberry bug (Jadera haematoloma) lives in the southeastern United States, with its range stretching from Florida to Oklahoma. It uses a needle-like beak to pierce the outside skin of fruit, and then pierce the seed coat of seeds within the fruit. Enzymes liquify the seeds, and the bugs suck up the liquified seed contents.
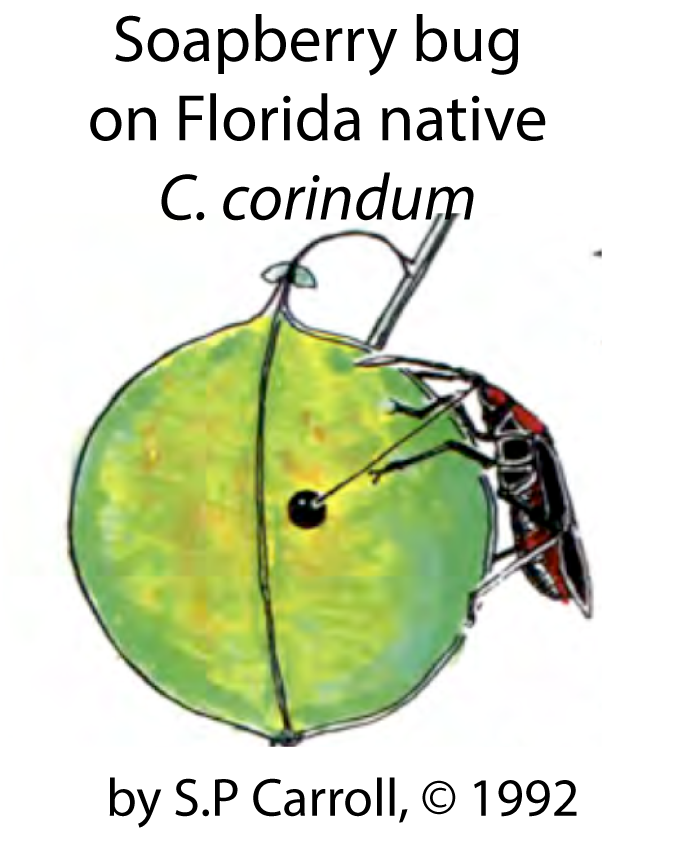
Here’s a drawing by UC Davis Professor Scott P. Carroll of a soapberry bug feeding on the fruit that’s native to Florida, Cardiospermum corindum. Note the distance between the fruit’s skin and its seed, and the corresponding length of the soapberry bug’s beak.
In historical times (within the last 150 years), several plant species have been introduced from Europe and Asia into the range of the soapberry bug. These introduced species have fruit in which the distance between the outside skin and the seeds inside is different from that of the native species. In Florida, the introduced species (Koelreuteria elegans) had a fruit structure in which the seeds were much closer to the skin of the fruit than in the Florida native, C. corindum.
In the interactive reading below, you can interpret what happened.
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Evidence for evo: soapberry bug”]
[h]Phenotype shifts in response to introduced host species in the soapberry bug
[i]Note that in this graph, the values above and below the 0 line are positive.
[q labels = “top”]The graph below shows how there’s a correlation between the distance between the wall of the fruit and the surface of the ________, and the length of the soapberry bug’s __________. The population with the __________ beaks are those which feed on the __________ fruit, in which there’s a greater distance between the fruit wall and the seed.
[l]beak
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]longest
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]native
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]seed
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[q labels = “top”]The table below shows what happened in Florida in soapberry bug populations that started feeding on the introduced species. Using logic and your understanding of natural selection, match the average beak length of the soapberry bugs with the plants they feed upon.
| Host Plant | Origin | Average distance from fruit wall to seed (mm) | Average beak length (mm) |
| Balloon Vine (C. corindum) | Native | 9.32 | _______ |
| Goldenrain tree (K. elegans) | Introduced | 2.82 | _______ |
[l]6.93
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]11.92
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[q labels = “bottom”]Let’s interpret these results. Note that the labels are below the paragraph.
| Host Plant | Origin | Average distance from fruit wall to seed (mm) | Average beak length |
| Balloon Vine (C. corindum) | Native | 9.32 | 11.92 |
| Goldenrain tree (K. elegans) | Introduced | 2.82 | 6.93 |
When soapberry bug populations colonized the introduced host (the Goldenrain tree), these populations ___________ to their host’s fruit structure. What’s notable is the ___________ with which this shift occurred: a few dozen _____________. Additionally, when eggs from one host were transplanted to the other, the offspring’s beaks maintained the length of the population from which the eggs were harvested. This shows that the shift in _____________ was based in an underlying ____________ change. (source: Campbell, Biology, 11th edition, page 475).
[l]adapted
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]generations
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[l]hereditary
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]phenotype
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[l]speed
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[q]To summarize. In the introduced fruit K. elegans the distance between the fruit wall and the seed is much [hangman] than in it is in the native fruit, C. corindum. In those populations of the soapberry bug that began to exploit the fruit of this new host, there was less [hangman] pressure for extremely long beaks. Bugs with [hangman] beaks experienced no loss of evolutionary [hangman] (and might have increased their fitness, since less energy was required to build a very long [hangman]. Within a few dozen generations, populations exploiting K. elegans had significantly shorter beaks than populations on the native fruit, making this a documented example of [hangman] with [hangman].
[c]bGVzcw==[Qq]
[c]c2VsZWN0aXZl[Qq]
[c]c2hvcnRlcg==[Qq]
[c]Zml0bmVzcw==[Qq]
[c]YmVhaw==[Qq]
[c]ZGVzY2VudA==[Qq]
[c]bW9kaWZpY2F0aW9u[Qq]
[/qwiz]
5. Cumulative Quiz: Historical Examples of Evolution
There are numerous examples of rapid evolutionary change that’s been observed by biologists. To learn more, use any of the following links
- This article in Discover Magazine has several examples.
- The evolution of the Peppered Moth. This is an example of industrial melanism first identified in the 1800s, confirmed by B.D. Kettlewell in the 1950s, subsequently attacked by creationists, then validated by experiments at the start of the 21st century by Michael Majerus). You can read about the scientific history and biology on Wikipedia. I have also produced a music video about the peppered moth.
- Species formation (also based on host shifts and introduced species) in the apple maggot fly.
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Evidence for Evo: historical examples”]
[h] Historical Examples of Evolutionary Change
[i]
[q] Because of the large body of evidence supporting evolution, it should be thought of as a [hangman], rather than a [hangman].
[c]IHRoZW9yeQ==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[c]IGh5cG90aGVzaXM=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] If evolution is true, then one should be able to provide evidence for descent with [hangman] in any specific lineage. For example, fossils would show that a currently existing species’ [hangman] are different from the current form of that species.
[c]IG1vZGlmaWNhdGlvbg==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[c]IGFuY2VzdG9ycw==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] If evolution is true, then a population’s [hangman] makeup should be changing over time.
[c]IGdlbmV0aWM=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q] The diagram below represents a situation in which species 1 through 9 all evolved from a common ancestor. If evolution is true, then the species 1 through 9 should share some traits in common. At the same time, in each lineage these traits might be [hangman] in different ways.
[c]IG1vZGlmaWVk[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q] Darwin thought that evolutionary change had to happen slowly. That makes him a [hangman]. However, observations of evolutionary change in the 19th, 20th, and 21st centuries indicate that evolutionary change can happen [hangman]: in a few decades.
[c]IGdyYWR1YWxpc3Q=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[c]IHF1aWNrbHk=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] Because of our overuse of antibiotics, many bacterial strains have become antibiotic [hangman].
[c]IHJlc2lzdGFudA==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, images A and B show how antibiotic resistance was pre-[hangman], and then [hangman] for by overuse of antibiotics.
[c]IGV4aXN0aW5n[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[c]IHNlbGVjdGVk[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q] In the diagram below, image D shows how antibiotic [hangman] in bacteria can spread through [hangman] gene transfer.
[c]IHJlc2lzdGFuY2U=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[c]IGhvcml6b250YWw=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] The difficult-to-treat strain of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria that has evolved in recent decades is known by the acronym [hangman].
[c]IE1SU0E=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q]Since its introduction in the 1940s, DDT has become increasingly ineffective due to the evolution of pesticide [hangman] in mosquitoes that carry the Plasmodium parasite which causes [hangman].
[c]cmVzaXN0YW5jZQ==[Qq]
[c]bWFsYXJpYQ==[Qq]
[q multiple_choice=”true”] True or false: In response to DDT, mosquitoes developed a mutation that made them resistant.
[c]IHRydWU=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBOYXR1cmFsIHNlbGVjdGlvbiBpcyBub3QgYWJvdXQgcG9wdWxhdGlvbnMgcHJvZHVjaW5nIG11dGF0aW9ucyB0aGF0IGhlbHAgdGhlbSBzdXJ2aXZlIGVudmlyb25tZW50YWwgY2hhbGxlbmdlcy4gSXQmIzgyMTc7cyBhYm91dCB0aGUgZW52aXJvbm1lbnQgc2VsZWN0aW5nIHZhcmlhbnQgcGhlbm90eXBlcyB0aGF0IG1ha2UgdGhlIGluZGl2aWR1YWxzIHdobyBoYXZlIHRoZW0gbW9yZSBzdWl0ZWQgdG8gc3Vydml2aW5nIGFuZCByZXByb2R1Y2luZy4gVGhlIG11dGF0aW9uIHByZWNlZGVzIHRoZSBjaGFsbGVuZ2Uu[Qq]
[c]IGZh bHNl[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gTmF0dXJhbCBzZWxlY3Rpb24gaXMgbm90IGFib3V0IHBvcHVsYXRpb25zIHByb2R1Y2luZyBtdXRhdGlvbnMgdGhhdCBoZWxwIHRoZW0gc3Vydml2ZSBlbnZpcm9ubWVudGFsIGNoYWxsZW5nZXMuIEl0JiM4MjE3O3MgYWJvdXQgdGhlIGVudmlyb25tZW50IHNlbGVjdGluZyB2YXJpYW50IHBoZW5vdHlwZXMgdGhhdCBtYWtlIHRoZSBpbmRpdmlkdWFscyB3aG8gaGF2ZSB0aGVtIG1vcmUgc3VpdGVkIHRvIHN1cnZpdmluZyBhbmQgcmVwcm9kdWNpbmcuIFRoZSBtdXRhdGlvbiBwcmVjZWRlcyB0aGUgY2hhbGxlbmdlLg==[Qq]
[q]Like the mosquito, the soapberry bug is an example of an insect that [hangman] quickly in response to selective [hangman]. In the case of the soapberry bug, populations that exploited a new food resource quickly changed their [hangman]. Specifically, the [hangman] length of soapberry bug populations became significantly [hangman] in a few decades.
[c]ZXZvbHZlZA==[Qq]
[c]cHJlc3N1cmU=[Qq]
[c]cGhlbm90eXBl[Qq]
[c]YmVhaw==[Qq]
[c]c2hvcnRlcg==[Qq]
[/qwiz]
Links
- Homologous and Vestigial Structures (the next tutorial in this module)
- Evidence for Evolution Menu
