Page outline
- Review: The Two Phases of Photosynthesis
- Video: The Energy Transformations of Photosynthesis
- Understanding Light
- Chlorophyll
- Absorption and Action Spectra
- Music Video: The Light Reactions Part 1
- The Light Reactions: Interactive Lyrics
- Quiz: Light and Photosynthetic Pigments
1. Review: the Two Phases of Photosynthesis
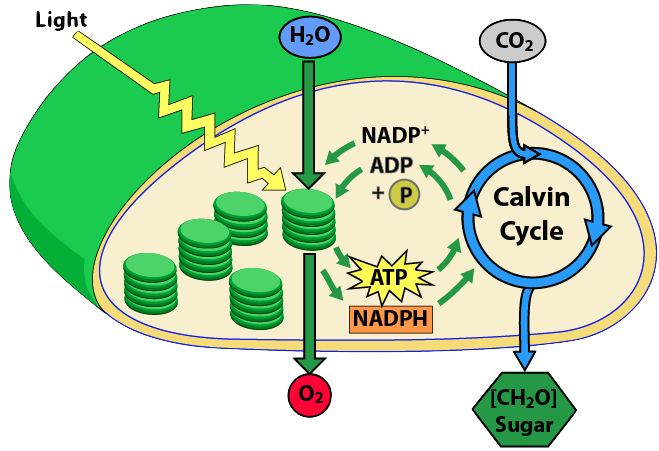 In the last module, we learned that photosynthesis occurs in two phases: the light reactions and the Calvin cycle. Here’s a summary of what happens in each.
In the last module, we learned that photosynthesis occurs in two phases: the light reactions and the Calvin cycle. Here’s a summary of what happens in each.
- The light reactions: Powered by energy from light, the chloroplast oxidizes water, reduces the electron carrier NADP+ to NADPH, and combines ADP and Pi to form ATP. Having lost electrons and protons, water becomes oxygen, which bubbles out of the chloroplast.
- The Calvin cycle: The chloroplast uses energy from ATP and reducing power from NADPH to reduce carbon dioxide to the three-carbon sugar G3P (glyceraldehyde phosphate), the key output of photosynthesis (and the molecule that could be considered to be the goal of the process). As carbon dioxide is reduced, NADPH is oxidized to become NADP+, and ATP loses energy to become ADP and Pi.
Now, let’s delve into some of the features of light and chlorophyll that make photosynthesis possible.
2. The Energy Transformations of Photosynthesis; Light, and Pigments
In photosynthesis, light energy is used to change carbon dioxide (a low-energy exhaust product) into carbohydrate (a high-energy fuel). Photosynthesis harvests light energy during the light reactions, which involve two energy conversions.
- First, light energy is converted into a flow of electrons: essentially, an electrical current.
- Second, that electrical current is converted into the chemical energy of two short-term energy-storage compounds: NADPH and ATP.
The video below explains what you need to understand about light and chlorophyll.
3. Understanding Light
Light is a form of electromagnetic energy. We commonly experience other forms of electromagnetic energy in our daily lives, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays.
As a biology student, you only need to know a few things about electromagnetic energy.
- It’s a type of energy that can move through the vacuum of space (unlike sound energy, for example, which needs to move through the air, water, and other fluids).
- It has a dual nature. On the one hand, electromagnetic energy consists of massless particles called photons. Thinking of this energy as particles is useful when you want to envision a photon hitting an electron and energizing it (which, as we’ll see, is what happens during photosynthesis). At the same time, electromagnetic energy is a wave, with a frequency and a wavelength.
- The wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic energy are inversely linked together: as frequency increases, the wavelength decreases (and vice versa). For example, X-rays have a very short wavelength (about 10-10 meters). Correspondingly, their frequency is very high (1018 Hertz, or waves/second).
- Higher frequency/shorter wavelength electromagnetic energy has more energy than lower frequency, longer wavelength energy. For example, X-rays have more energy than radio waves. As a result, we take protective measures against needless exposure to X-rays when X-rays are used in medical or dental settings. That’s because the energy from X-rays can disrupt DNA and proteins, causing tissue damage and mutations that have been associated with cancer. But we don’t worry about exposure to radio waves (which are constantly passing through our bodies).
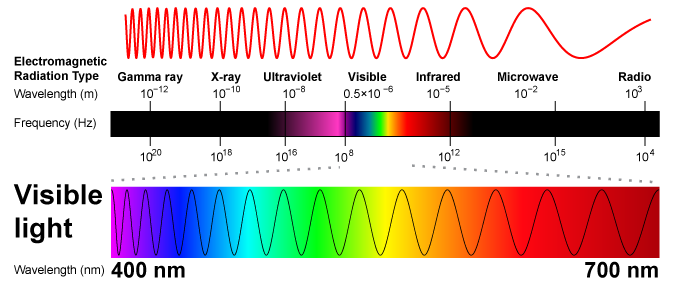
The diagram above illustrates the connection between electromagnetic energy, wavelength, and frequency. In terms of photosynthesis, it also shows how visible light is just one portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. It’s the portion that our primate visual system evolved to see, and which photosynthetic organisms evolved to exploit for converting electromagnetic energy into chemical energy.
Like all electromagnetic energy, light consists of photons that have a wavelength and a frequency (though only the wavelength is indicated in this image). Note that red light has a longer wavelength (700 nm) than violet light (400 nm). That means that red light has less energy than violet light.
 Also, note that in our daily lives, we rarely experience light of only one wavelength. White light from a light bulb is a mixture of wavelengths, as is the light from the sun (which also includes many other wavelengths of electromagnetic energy, ranging from radio waves to X-rays). When we shine a beam of white light through a prism, however, we can see how it breaks up into its constituent colors. In nature, that happens whenever we see a rainbow.
Also, note that in our daily lives, we rarely experience light of only one wavelength. White light from a light bulb is a mixture of wavelengths, as is the light from the sun (which also includes many other wavelengths of electromagnetic energy, ranging from radio waves to X-rays). When we shine a beam of white light through a prism, however, we can see how it breaks up into its constituent colors. In nature, that happens whenever we see a rainbow.
4. Chlorophyll: the key photosynthetic pigment

When light (and all electromagnetic energy) interacts with matter, the energy can be reflected or absorbed. Substances called pigments absorb certain light wavelengths and reflect others. So, what does it mean for something to be green, blue, or yellow? Because we’re dealing with photosynthesis, which is carried out by green plants, let’s focus on green. A green object is perceived as green because it has pigments that reflect green light (which bounces off the pigmented object into our eyes) and absorb other wavelengths of light. That means that the green leaves of plants are reflecting away green light, and absorbing other wavelengths, such as blue and red.
In chloroplasts, the primary photosynthetic pigment is chlorophyll. Chlorophyll molecules have a central magnesium atom (at “3”), essential for the process of converting light energy into electrical energy. The magnesium atom is embedded within a nitrogenous porphyrin ring (“2”). A long hydrocarbon chain anchors chlorophyll in the thylakoid membrane.
The methyl group (-CH3) shown at “4” is what makes this chlorophyll “chlorophyll a.” Another chlorophyll, chlorophyll b, has the same structure, except for that at number “4” it would have a carbonyl group (a –C=O: carbon double bonded to an oxygen) instead of the methyl group. That chemical change has the effect of changing which wavelengths of light the chlorophyll absorbs, as we’ll see below.
5. Absorption and Action Spectra
Chlorophyll’s properties as a pigment can be quantified through its absorption spectrum. In a laboratory setting, you can take isolated chlorophyll, and, using a device like a spectrophotometer, you can measure which wavelengths of light chlorophyll best absorbs. Why is this important? Because the wavelengths of light that a pigment absorbs can be harvested to perform some work. In the case of photosynthesis, the work is creating an electrical current, which can be used to transform lower energy molecules into higher energy molecules.
Here’s the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a. The X-axis shows the wavelength of light shining on the chlorophyll, and it ranges from short-wavelength violet light at 400 nm (“nm” = nanometer, or 1 billionth of a meter) on the far left to 760 nm red light on the far right. The Y-axis is the percentage of absorption of light energy.
The part of the line bracketed by “b” shows how in the green and yellow part of the spectrum chlorophyll a absorbs hardly any light. By contrast, the highest point of the line (“a”) is where most light energy is absorbed (blue light). A second peak shows up in the red part of the spectrum at “c.”
The graph below adds two additional photosynthetic pigments: Chlorophyll b and carotenoids. Carotenoids are accessory pigments: they help absorb light energy during photosynthesis, and they protect the photosynthetic pigments (in much the same way that the pigment melanin protects DNA in our skin cells from damage from ultraviolet radiation).

The absorption spectrum for a pigment shows how much light energy a pigment absorbs. By contrast, the action spectrum shows how much photosynthesis occurs at different wavelengths of light. In other words, an absorption spectrum is a property of a pigment. An action spectrum is a property of a photosynthesizing organism (or of isolated chloroplasts).
How could you measure how much photosynthesis occurs at different wavelengths of light? It’s pretty straightforward, and there are many AP, college, or high school level lab activities where you do exactly that. One involves using disks from spinach leaves (cut out with a paper hole punch) and placed in water. As the disks photosynthesize, they produce bubbles of oxygen, which makes them float. You can measure how long it takes for the disks to float to the top of a cup of water, and that gives you an indication of how much photosynthesis is occurring.
The action spectrum for photosynthesis looks like what you see below.
The X-axis of this graph is the same as the absorption spectra graphs above. The Y-axis now shows oxygen production. You can see that the highest amount of photosynthesis occurs at about 700 nm, in the red part of the spectrum (at “C”). Yellow light (at “b”) generates the least amount of photosynthesis. Another peak is the blue part of the spectrum at “a.”
6. Music Video: The Light Reactions, Part One
The music video below covers
- 00:21: The Two Phases of Photosynthesis (Light Reactions and Calvin Cycle)
- 00:41: Chorus with animation of entire light reactions
- 00:56: Chloroplast structure (stroma, thylakoids, thylakoid membranes)
- 01:16: Photosynthetic pigments/chlorophyll structure
- 01:48: Chorus
- 02:03: Action spectrum/Englemann’s experiment; Comparison with Absorption Spectrum
- 02:45: Chorus
7 Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions Part 1, Interactive Lyrics
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Light Reactions 1, Interactive Lyrics (2.0)”]
[h]Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions Part 1, Interactive Lyrics
[i]These are the lyrics to Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions, Part 1, organized into a fill-in-the-blanks quiz. Reading like this will deepen your understanding of how photosynthesis works.
[q labels = “top” dataset_id=”SMV_Light_Rxns_Part_1_Interactive_Lyrics|d1c5f92487bb4″ question_number=”1″]
Organisms like plants that ___________________
Chemically combine water with carbon dioxide
Making _________________ and oxygen too,
That’s why photosynthesis should matter to you!
The light reactions are photosynthesis’s first phase
The output’s ATP and _________
O2‘s the by-product, and as you can see
The inputs are water, and _______________.
Using up the ATP and the NADPH,
While absorbing CO2 (it’s carbon _________)
Photosynthesis, what a sensation
[l]Calvin
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]carbohydrates
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[l]fixation
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]light energy
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]NADPH
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]photosynthesize
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[q labels = “top” dataset_id=”SMV_Light_Rxns_Part_1_Interactive_Lyrics|d1bf9203d4bb4″ question_number=”2″]
Light reactions
happening in leaves
Making _________
NADPH and ATP.
Through a _______-charged
current of electricity
Converted into ___________ energy
[l]chemical
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[l]oxygen
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]solar
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[q labels = “top” dataset_id=”SMV_Light_Rxns_Part_1_Interactive_Lyrics|d1b8261dedfb4″ question_number=”3″]
Chloroplasts are the photosynthesizing organelle.
You can find them in leaves, in a _____________ cell,
Inside chloroplasts is a fluid called _______,
it’s true everywhere, from Tokyo to Roma.
The stroma bathes tiny sacs called ___________,
Membrane bound sacs, with a tiny space inside,
The thylakoid’s membrane is loaded with protein
It’s the _________________’ main scene
It also has pigments like green ______________
Orange carotenoids and yellow xanthophylls
These pigments ________ light that’s mostly red and blue
The green is not absorbed it reflects back to you.
[l]absorb
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]chlorophylls
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]light reactions
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]mesophyll
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[l]stroma
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[l]thylakoids
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[q labels = “top” dataset_id=”SMV_Light_Rxns_Part_1_Interactive_Lyrics|d1b129fa41fb4″ question_number=”4″]
Every chlorophyll has a ____________ ring,
With magnesium atoms in the center of that thing.
In the light reactions that magnesium gets pinged,
By photons, making its ___________ zing,
Notice the chlorophyll’s tail — a _______________ chain
Which anchors chlorophyll into the thylakoid membrane.
A molecule with style, so pretty,
In the thylakoid, it makes ___________.
[l]electricity
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[l]electrons
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[l]hydrocarbon
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[l]porphyrin
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[q labels = “top” dataset_id=”SMV_Light_Rxns_Part_1_Interactive_Lyrics|d1aa2dd695fb4″ question_number=”5″]
Engelmann showed us the _______ spectrum
He used a prism to break the sun’s
Light into its many different _______,
Shone it on an algae called Cladophora
The O2 algae makes will stimulate bacteria
Which will grow in any ________ -rich area
Bacteria loved it over blue and red
But hardly grew over _______, they might as well be dead!
[l]action
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Great!
[l]colors
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[l]green
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]oxygen
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Good!
[q labels = “top” dataset_id=”SMV_Light_Rxns_Part_1_Interactive_Lyrics|d19eaedbe03b4″ question_number=”6″]
This line of growth, it’s a reflection,
Of ___________________ action spectrum
Note this doesn’t match exactly
The absorption spectra of ______________ a or b.
‘Cause the carotenoids and _______________ we´ve met
Absorb light frequencies the chlorophylls can´t get,
And in the ___________ they all cooperate
In making ATP and NADPH.
[l]chlorophyll
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Excellent!
[l]photosynthesis’s
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]thylakoid
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[l]xanthophylls
[fx] No. Please try again.
[f*] Correct!
[/qwiz]
8. Quiz – Photosynthesis: Light and Pigments
At this point, we’ve identified a few key things about photosynthesis:
- its energy conversions
- its key pigment
- the absorption spectra associated with some of its key pigments
- its action spectrum.
And we’ve discussed a few key features of the light energy that drives photosynthesis.
Let’s take a quiz, and then, in the next tutorial, we’ll learn about the details of the light reactions.
[qwiz random = “true” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Light and Pigments (2.0)”]
[h]Photosynthesis: Light and Pigments
[i]
[q multiple_choice=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|704d139a795e4″ question_number=”1″] Light energy directly drives the transformation of
[c]IE5BRFBIIGludG8gTkFEUA==Kw==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBOQURQSCBpbnRvIE5BRFA=Kw==IGlzIG94aWRhdGlvbiwgYW5kIGl0IGxvd2VycyBmcmVlIGVuZXJneS4gTGlnaHQgZW5lcmd5IGlzIHVzZWQgdG8gaW5jcmVhc2UgZnJlZSBlbmVyZ3kuIE5leHQgdGltZSwgbWFrZSBhbm90aGVyIGNob2ljZS4=[Qq]
[c]IE5BRFA=Kw==IGludG8gTkFEUEg=[Qq]
[f]IFlvdSYjODIxNztyZSBwYXJ0aWFsbHkgY29ycmVjdCwgYnV0IHRoZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBiZXR0ZXIgYW5zd2VyICh0aGVyZSYjODIxNztzIHNvbWV0aGluZyBlbHNlIHRoYXQgbGlnaHQgZW5lcmd5IGRvZXMu[Qq]
[c]IEFUUCBpbnRvIEFEUCBhbmQgcGhvc3BoYXRl[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUaGF0JiM4MjE3O3MgYW4gZXhlcmdvbmljIHJlYWN0aW9uIHRoYXQgZG9lc24mIzgyMTc7dCBuZWVkIGFueSBkcml2ZXIuIExvb2sgZm9yIGVuZGVyZ29uaWMgcmVhY3Rpb25z[Qq]
[c]IEFEUCBhbmQgUCBpbnRvIEFUUA==[Qq]
[f]IFlvdSYjODIxNztyZSBvbiB0aGUgcmlnaHQgdHJhY2ssIGJ1dCB0aGVyZSYjODIxNztzIGEgYmV0dGVyIGFuc3dlci4gRmluZCBpdA==[Qq]
[c]IEFEUCBhbmQgUCBpbnRv IEFUUDsgYW5kwqBOQURQKw==IGludG8gTkFEUEg=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gVGhvc2UgYXJlIHRoZSB0d28gZGlyZWN0IHByb2R1Y3RzIG9mIHRoZSBsaWdodCByZWFjdGlvbnMu
Cg==[Qq]
[q multiple_choice=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|704925c6689e4″ question_number=”2″] Photosynthesis converts
[c]IGVsZWN0cmljYWwgZW5lcmd5IHRvIGNoZW1pY2FsIGVuZXJneSB0byBsaWdodCBlbmVyZ3k=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBSZW1lbWJlciB0aGF0IHBob3Rvc3ludGhlc2lzIG1lYW5zICYjODIyMDttYWtpbmcgd2l0aCBsaWdodC4mIzgyMjE7IFRoZSBwcm9jZXNzIHN0YXJ0cyB3aXRoIGxpZ2h0LiBSZW1lbWJlciB0aGF0IHRoZSBuZXh0IHRpbWUgeW91IHNlZSB0aGlzIHF1ZXN0aW9uLg==[Qq]
[c]IGNoZW1pY2FsIGVuZXJneSB0byBsaWdodCBlbmVyZ3kgdG8gZWxlY3RyaWNhbCBlbmVyZ3k=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUbyBiZWdpbiB3aXRoLCBwaG90b3N5bnRoZXNpcyBzdGFydHMgd2l0aCBsaWdodCBlbmVyZ3kuIFJlbWVtYmVyIHRoYXQgYW5kIG1ha2UgYW5vdGhlciBjaG9pY2UgbmV4dCB0aW1lLg==[Qq]
[c]IGxpZ2h0IGVuZXJneSBpbnRvIGVsZWN0cmljYW wgZW5lcmd5IGludG8gY2hlbWljYWwgZW5lcmd5[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gTGlnaHQgdG8gZWxlY3RyaWNpdHkgdG8gY2hlbWljYWwgZW5lcmd5OiB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3MgcGhvdG9zeW50aGVzaXMu
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|70458273d45e4″ question_number=”3″] Light is a type of [hangman] energy
[c]IGVsZWN0cm9tYWduZXRpYw==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|7041df21401e4″ question_number=”4″] Particles of light energy are called [hangman].
[c]IHBob3RvbnM=[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|703e610f6a1e4″ question_number=”5″] Unlike sound, electromagnetic energy can move through the [hangman]of space.
[c]IHZhY3V1bQ==[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|703ae2fd941e4″ question_number=”6″] As the frequency of light increases, its [hangman]shortens
[c]IHdhdmVsZW5ndGg=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|70371a6a419e4″ question_number=”7″] The wavelength of blue light is [hangman]than the wavelength of red light.
[c]IHNob3J0ZXI=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|70337717ad5e4″ question_number=”8″] The type of electromagnetic radiation that we can see is[hangman]
[c]IGxpZ2h0[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|702fd3c5191e4″ question_number=”9″] Substances that absorb or reflect electromagnetic radiation (including light) are called [hangman]
[c]IHBpZ21lbnRz[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|702c307284de4″ question_number=”10″] The key pigment in photosynthesis is[hangman].
[c]IGNobG9yb3BoeWxs[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|7028429e741e4″ question_number=”11″] The part that anchors chlorophyll in the thylakoid membrane is
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID E=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gJiM4MjIwOzEmIzgyMjE7IGlzIGEgaHlkcm9jYXJib24gdGFpbCwgd2hpY2ggYW5jaG9ycyBjaGxvcm9waHlsbCBpbiB0aGUgdGh5bGFrb2lkIG1lbWJyYW5lLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUaGluayBhYm91dCBob3cgbWVtYnJhbmVzIGFyZSBtYWRlIG9mIHBob3NwaG9saXBpZHMsIHdoaWNoIGluY2x1ZGUgbG9uZyBoeWRyb2NhcmJvbiBjaGFpbnMuIFdoYXQgcGFydCBvZiBhIGNobG9yb3BoeWxsIG1vbGVjdWxlIGlzIGxpa2UgYSBsb25nIGh5ZHJvY2FyYm9uIGNoYWluPw==
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|70242f89a51e4″ question_number=”12″] The porphyrin ring is
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID I=[Qq]
[f]IE5pY2UuICYjODIyMDsyJiM4MjIxOyBpcyBhIHBvcnBoeXJpbiByaW5nLiBUaGVzZSBzdHJ1Y3R1cmVzIGFyZSBrZXkgdG8gbGlmZSwgYXMgdGhleSBwbGF5IGEgcm9sZSBpbiBiaW9sb2dpY2FsIHBpZ21lbnRzIGxpa2UgY2hsb3JvcGh5bGwsIGFuZCBhbHNvIGluIG1vbGVjdWxlcyBsaWtlIGhlbW9nbG9iaW4sIG15b2dsb2JpbiwgYW5kIGN5dG9jaHJvbWVzLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUaGlzIGlzIGp1c3QgcHVyZSBtZW1vcml6YXRpb24uIFBvcnBoeXJpbnMgYXJlIHdvcnRoIGtub3dpbmcgYWJvdXQgYmVjYXVzZSB0aGV5IGFwcGVhciBub3Qgb25seSBpbiBjaGxvcm9waHlsbCwgYnV0IGFsc28gbW9sZWN1bGVzIGxpa2UgaGVtb2dsb2JpbiwgbXlvZ2xvYmluLCBhbmQgY3l0b2Nocm9tZXMuIE5leHQgdGltZSwgbm90ZSB0aGF0IGl0JiM4MjE3O3MgY2FsbGVkIGEgcG9ycGh5cmluIHJpbmcuIFdoZXJlIGRvIHlvdSBzZWUgYW55dGhpbmcgdGhhdCBsb29rcyBsaWtlIGEgcmluZyBvZiBhIHBhcnRpY3VsYXIgZWxlbWVudD8=
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|70201c74d61e4″ question_number=”13″] Shifting one functional group in chlorophyll changes its absorption spectrum. Which number below indicates the changeable functional group?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID Q=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gJiM4MjIwOzQmIzgyMjE7IGlzIGEgbWV0aHlsIGdyb3VwLCB0aGUgcHJlc2VuY2Ugb2Ygd2hpY2ggbWFrZXMgdGhpcyBjaGxvcm9waHlsbCA=YQ==Lg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBIZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBoaW50LiBBIGZ1bmN0aW9uYWwgZ3JvdXAgaXMgYSBzbWFsbCBncm91cCBvZiBhdG9tcyB0aGF0IGNoYW5nZXMgdGhlIHByb3BlcnRpZXMgb2YgdGhlIGxhcmdlciBtb2xlY3VsZSB0aGF0IGl0JiM4MjE3O3MgYXR0YWNoZWQgdG8uIFRoZXJlJiM4MjE3O3Mgb25seSBvbmUgZnVuY3Rpb25hbCBncm91cCBzaG93biBpbiB0aGUgZGlhZ3JhbSBhYm92ZS4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|701b999dcc5e4″ question_number=”14″] In the diagram below, the letter indicating the lowest absorption is
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]IG I=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gTGV0dGVyICYjODIyMDtiJiM4MjIxOyBzaG93cyB0aGUgbG93ZXN0IGxldmVsIG9mIGFic29yYmFuY2UsIHdoaWNoIGZvciB0aGlzIG1vbGVjdWxlIChjaGxvcm9waHlsbCBhKSBpcyBpbiB0aGUgeWVsbG93LWdyZWVuIHBhcnQgb2YgdGhlIHNwZWN0cnVtLg==[Qq]
[c]ICo=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBZb3UgY2FuIGhhbmRsZSB0aGlzIHF1ZXN0aW9uIGJ5IHJlbWVtYmVyaW5nIHRoYXQgeWVsbG93L2dyZWVuIGxpZ2h0IGlzIHRoZSBsaWdodCB3YXZlbGVuZ3RoIGxlYXN0IGFic29yYmVkIGJ5IGNobG9yb3BoeWxsLiBPciwganVzdCB0YWtlIGEgZ29vZCBsb29rIGF0IHRoZSBncmFwaCwgYW5kIG5vdGUgdGhlIGxvd2VzdCBsZXZlbCBvZiBhYnNvcmJhbmNlLg==[Qq]
[q multiple_choice=”true” dataset_id=”SMV_PSN_light_and_pigments|701373742e5e4″ question_number=”15″] Students set up an experiment in which they shine blue, green, and red light on disks of spinach leaves, and determine the amount of photosynthetic activity by measuring oxygen the disks produce. Which of the colors below will generate the least photosynthetic activity
[c]IGJsdWU=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBOZXh0IHRpbWUsIHRoaW5rIGFib3V0IHRoZSBhY3Rpb24gc3BlY3RydW0gZm9yIHBob3Rvc3ludGhlc2lzIGFuZCBjaG9vc2UgYSBkaWZmZXJlbnQgY29sb3Iu[Qq]
[c]IGdy ZWVu[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4gSWYgeW91IHRoaW5rIG9mIHRoZSBhY3Rpb24gc3BlY3RydW0gZm9yIHBob3Rvc3ludGhlc2lzLCBncmVlbiBpcyB0aGUgY29sb3Igb2YgbGlnaHQgdGhhdCBkcml2ZXMgdGhlIGxlYXN0IGFtb3VudCBvZiBwaG90b3N5bnRoZXRpYyBhY3Rpdml0eS4=[Qq]
[c]IHJlZA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBOZXh0IHRpbWUsIHRoaW5rIGFib3V0IHRoZSBhY3Rpb24gc3BlY3RydW0gZm9yIHBob3Rvc3ludGhlc2lzIGFuZCBjaG9vc2UgYSBkaWZmZXJlbnQgY29sb3Iu[Qq]
[/qwiz]
What’s next?
- Proceed to Topic 3.4, Part 4: The Light Reactions (the next tutorial in AP Bio Unit 3)
