1. Watch this Video
2.a. READ THIS: A few ideas that didn’t make it into the video
- Cellular respiration is an oxidation-reduction process. Don’t let the chemistry scare you. All you need to know is that
- Oxidation involves the loss of electrons (and hydrogens) from energy-rich compounds. The oxidations in cellular respiration release energy that is ultimately used to create ATP.
- Reduction involves the gain of electrons. The reductions in cellular respiration are used to temporarily store energy in mobile electron carriers like NADH and FADH2, which deliver energetic electrons to the electron transport chain (explained a bit below, but mostly in the next tutorials)
- Cellular respiration is about making ATP from ADP and phosphate. During cellular respiration, ATP is made in two ways
- Substrate-Level Phosphorylation. During this process, which occurs during glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle, enzymes transfer a phosphate group from an organic substrate onto ADP, as shown below.
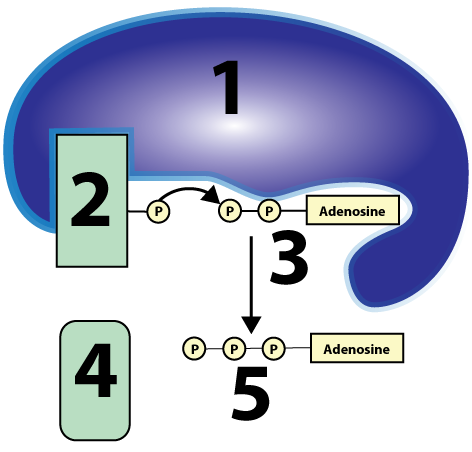
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation: 1-an enzyme; 2-a phosphate group attached to an organic substrate; 3-ADP; 4-substrate without a phosphate; 5-ATP
- Oxidative phosphorylation. During oxidative phosphorylation, the oxidation of mobile electron carriers provides the energy used to generate ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation is associated with two processes described below (and in other modules in this unit): the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
- Substrate-Level Phosphorylation. During this process, which occurs during glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle, enzymes transfer a phosphate group from an organic substrate onto ADP, as shown below.
2.b. Study this Summary
Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP)
- Cellular respiration is an exergonic reaction, releasing energy and increasing disorder by breaking down an organized glucose molecule into less organized products (CO2 and H2O).
Location of Cellular Respiration in Eukaryotic Cells
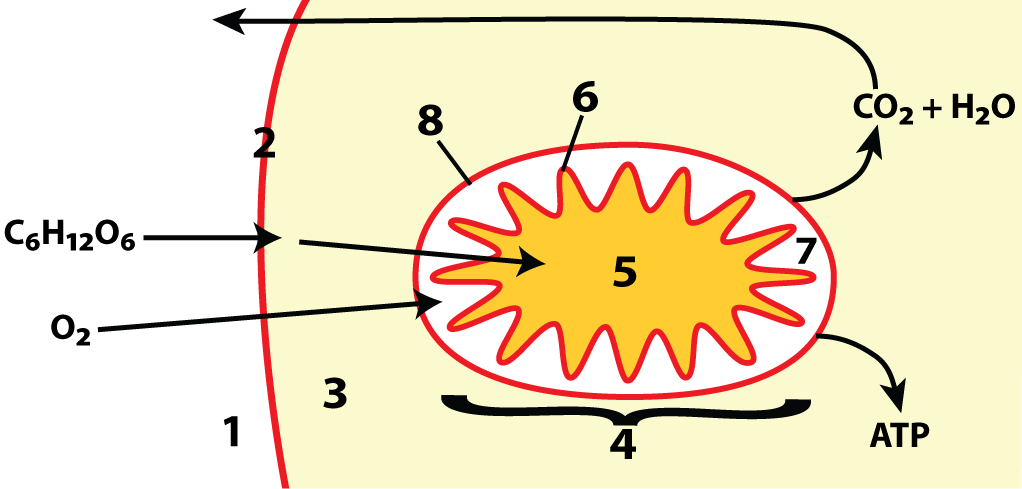
1-cell exterior; 2-membrane; 3-cytoplasm (where glycolysis occurs);
4-mitochondrion; 5-matrix (where the Link Reaction and Krebs occurs); 6-mitochondrial inner membrane (where electron transport chain occurs); 7-intermembrane space (key for chemiosmosis);
8-outer membrane
- Glycolysis: Occurs in the cytoplasm.
- Link Reaction: Transfers the product of glycolysis into the mitochondrial matrix.
- Krebs Cycle: Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain): Occurs along the mitochondrial membrane using the intermembrane space for a chemiosmotic gradient.
Phases of Cellular Respiration
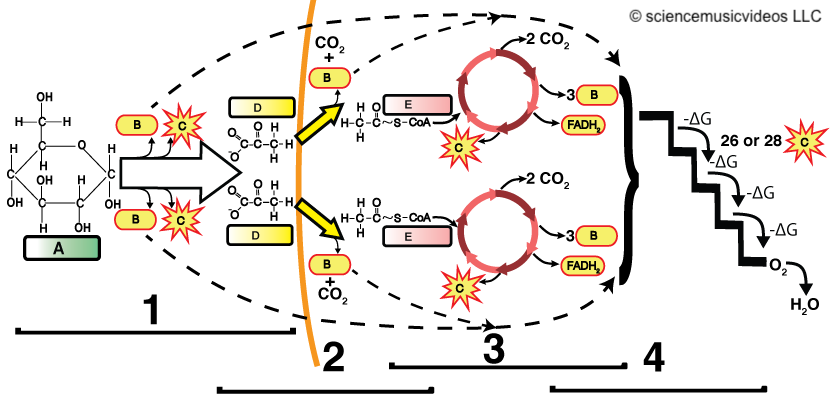
1-glycolysis; 2-link reaction; 3-Krebs cycle; 4-Electron Transport Chain/Chemiosmosis;
A-glucose; B-ATP; C-NADH; D-pyruvate; E-acetyl-CoA
Glycolysis
- Breaks down glucose (6 carbons) into two pyruvate molecules (3 carbons each).
- Produces a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH (electron carriers).
Link Reaction
- Pyruvate enters the mitochondrial matrix.
- Enzymes convert pyruvate to acetyl-CoA (2 carbons) by releasing one CO2 . This is 1/3 of the carbon dioxide you release when you exhale.
- Generates NADH for use in the electron transport chain.
Krebs Cycle
- Oxidizes acetyl-CoA, releasing 2 CO2 . This is the remaining 2/3 of the carbon dioxide you release when you exhale.
- Produces:
- 3 NADH
- 1 FADH2 (another electron carrier)
- 1 ATP
- The cycle runs twice per glucose molecule.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
- Oxidizes NADH and FADH2, creating electron flow.
- Uses chemiosmosis to power ATP synthesis from ADP and phosphate.
- Produces the majority of ATP during cellular respiration.
3. Master these Flashcards
[qdeck bold_text=”false” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Cellular Respiration Overview Flashcards, APBVP”]
[h]Cellular Respiration Overview Flashcards
[i]
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP)
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2a01″ question_number=”1″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] What is cellular respiration?
[a] Cellular respiration is an oxidation-reduction process that breaks down glucose into CO2 and H2O, releasing energy that is used to make ATP.
[q]Write the word equation for cellular respiration, showing the inputs and outputs.
[a]glucose + oxygen → ATP + carbon dioxide + water
[q]Write the balanced chemical equation for cellular respiration
[a]C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP)
[q]The function of cellular respiration is the production of ______. The molecule that provides the chemical energy to to this is ____________
[a]The goal of cellular respiration is the production of ATP. The molecule that provides the chemical energy to do this is glucose.
[q]What are the two exhaust products of cellular respiration.
[a]The exhaust products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide and water.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2a02″ question_number=”2″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] What is oxidation, and where do oxidations occur during cellular respiration?
[a] Oxidation involves the loss of electrons (and hydrogens) from energy-rich compounds. During cellular respiration, glucose and its by-products are oxidized to create mobile electron carriers (NADH and FADH2). In the last phase of cellular respiration, these mobile electron carriers are mobilized release energy that powers the electron transport chain, which creates most of the ATP that’s created during cellular respiration.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2a03″ question_number=”3″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] What is reduction, and when do reductions happen during cellular respiration?
[a] Reduction involves the gain of electrons (and hydrogens). Reductions in cellular respiration store energy in mobile electron carriers like NADH and FADH2, which deliver electrons to the electron transport chain.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2a04″ question_number=”4″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] How is ATP made during cellular respiration?
[a] ATP is made in two ways:
– Substrate-Level Phosphorylation: Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from an organic substrate onto ADP (occurs in glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle).
– Oxidative Phosphorylation: The oxidation of electron carriers powers ATP synthesis via the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2b02″ question_number=”6″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] Is cellular respiration endergonic or exergonic?
[a] Cellular respiration is exergonic, releasing energy and increasing disorder by breaking down glucose into less organized products (CO2 and H2O).
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2b03″ question_number=”7″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] Where do the phases of cellular respiration occur in eukaryotic cells?
[a]
– Glycolysis: Cytoplasm
– Link Reaction: Mitochondrial matrix
– Krebs Cycle: Mitochondrial matrix
– Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain): Mitochondrial membrane and intermembrane space
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2b04″ question_number=”8″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] What happens during glycolysis?
[a]
– Glucose (6 carbons) is broken down into two pyruvate molecules (3 carbons each).
– Produces a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH (electron carriers).
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2b05″ question_number=”9″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] What happens during the link reaction?
[a]
– Pyruvate enters the mitochondrial matrix.
– Enzymes convert pyruvate to acetyl-CoA (2 carbons), releasing one CO2.
– Enzymes oxidize pyruvate, reducing NADH for the electron transport chain.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2b06″ question_number=”10″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] What happens during the Krebs Cycle?
[a]During the Krebs Cycle
- Enzymes oxidize acetyl-CoA, releasing 2 CO2.
- Produces:
- 3 NADH
- 1 FADH2
- 1 ATP
- Runs twice per glucose molecule.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”3.Cellular_Energetics” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|2b07″ question_number=”11″ topic=”3.6.Cellular_Respiration”] What happens during the electron transport chain (ETC)?
[a]During the ETC
- Oxidizes NADH and FADH2, creating electron flow.
- Powers chemiosmosis to synthesize ATP from ADP and phosphate
- Produces the majority of ATP during cellular respiration.
[x][restart]
[/qdeck]
4. Tackle these Quizzes
4.1. Where Cellular Respiration Happens, and Substrate Level Phosphorylation
[qwiz random = “true” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Cellular Respiration Overview and Substrate Level Phosphorylation, APBVP”]
[h]Cellular Respiration Overview and Substrate Level Phosphorylation
[i]
[q]Which number is the cell membrane?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq Ay[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcMuKAnSBpcyB0aGXCoGNlbGwgbWVtYnJhbmU=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uwqBUaGUgbWVtYnJhbmUgaXMgdGhlIGNlbGwmIzgyMTc7cyBvdXRlciBib3VuZGFyeS4gSWYgdGhlIGdsdWNvc2UgYW5kIG94eWdlbiAoQw==Ng==SA==MTI=Tw==[Qq]6 6O2) are outside the cell, and the cytoplasm is at “3,” then what number would be representing the membrane?
[q]Which number is the cytoplasm?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq Az[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcM+KAnSBpcyB0aGXCoGN5dG9wbGFzbS4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uwqBUaGUgY3l0b3BsYXNtIGlzIHRoZSBmbHVpZCByZWdpb24gYmV0d2VlbiB0aGUgY2VsbCYjODIxNztzIG1lbWJyYW5lIGFuZCB0aGUgbnVjbGV1cyAod2hpY2ggaXNuJiM4MjE3O3Qgc2hvd24gaW4gdGhpcyBkaWFncmFtKS4gV2hpY2ggbnVtYmVyIGlzIGp1c3QgaW5zaWRlIHRoZSBtZW1icmFuZSAoYnV0IG5vdCBwYXJ0IG9mIGFueSBvdGhlciBzdHJ1Y3R1cmUpPw==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which number is the mitochondrion?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq A0[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcNOKAnSBpcyB0aGUgbWl0b2Nob25kcmlvbi4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIExvb2sgZm9yIHRoZcKgY2VsbC1saWtlIG9yZ2FuZWxsZSBpbnNpZGUgdGhlIGN5dG9wbGFzbS4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which number is the mitochondrial matrix?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID U=[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcNeKAnSBpcyB0aGUgbWF0cml4Lg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uwqBUaGXCoG1hdHJpeCBpcyBhbmFsb2dvdXMgdG8gdGhlIGN5dG9wbGFzbSBvZiBhwqBtaXRvY2hvbmRyaW9uLiBJZiB0aGF0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGVub3VnaCBvZiBhIGhpbnQsIGl0JiM4MjE3O3MgdGhlIHJlZ2lvbiBpbnNpZGUgb2YgYcKgbWl0b2Nob25kcmlvbiYjODIxNztzIGlubmVyIG1lbWJyYW5lLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which number is the mitochondrial inner membrane?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq A2[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcNuKAnSBpcyB0aGUgbWl0b2Nob25kcmlhbCBpbm5lciBtZW1icmFuZS4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFN0YXJ0IGJ5IGZpbmRpbmcgYSBtaXRvY2hvbmRyaW9uICh0aGUgb25seSBzdHJ1Y3R1cmUgc2hvd24sIGluIHRoaXMgZGlhZ3JhbSwgaW5zaWRlIHRoZSBjZWxsKS4gTm90ZSB0aGF0IGl0IGhhcyB0d28gbWVtYnJhbmVzLiBUaGUgaW5uZXIgb25lIGlzIGhpZ2hseSBmb2xkZWQu
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which number is the intermembrane space?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq A3[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcN+KAnSBpcyB0aGXCoGludGVybWVtYnJhbmUgc3BhY2Uu[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uwqBUaGUgaW50ZXJtZW1icmFuZSBzcGFjZSBpcyB0aGUgcmVnaW9uIG9mIGEgbWl0b2Nob25kcmlvbiBpbi1iZXR3ZWVuIHRoZSBpbm5lciBhbmQgb3V0ZXIgbWVtYnJhbmUuIElmIHRoZSBtaXRvY2hvbmRyaW9uIGl0c2VsZiBpcyBhdCAmIzgyMjA7NCwmIzgyMjE7IHRoZW4gd2hhdCBudW1iZXIgd291bGQgYmUgdGhlIGludGVybWVtYnJhbmUgc3BhY2U/
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which number is the mitochondrial outer membrane?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq A4[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcOOKAnSBpcyB0aGUgbWl0b2Nob25kcmlhbCBvdXRlciBtZW1icmFuZS4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uwqBUaGUgb3V0ZXIgbWl0b2Nob25kcmlhbCBtZW1icmFuZSBpc8KgdGhlIHNlbGVjdGl2ZWx5IHBlcm1lYWJsZSBiYXJyaWVyIHRoYXQgc2VwYXJhdGVzIHRoZSBtaXRvY2hvbmRyaW9uICgmIzgyMjA7NCYjODIyMTspIGZyb20gdGhlIGN5dG9wbGFzbSAoJiM4MjIwOzMmIzgyMjE7KS4gS2VlcGluZyBpbiBtaW5kIHRoZSBmYWN0IHRoYXQgbWl0b2Nob25kcmlhIGhhdmUgYSBkb3VibGUgbWVtYnJhbmUsIHdoaWNoIG51bWJlciBoYXMgdG8gYmUgdGhlIG91dGVyIG9uZT8=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which number is the outside of the cell?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq Ax[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcMeKAnSBpcyB0aGUgb3V0c2lkZSBvZiB0aGUgY2VsbC4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIFRoZSBvdXRzaWRlIG9mIHRoZSBjZWxsLCBvciBjZWxsIGV4dGVyaW9yLCBpcyB0aGUgcmVnaW9uIG91dHNpZGUgb2YgdGhlIGNlbGwmIzgyMTc7cyBtZW1icmFuZS4gV2hhdCYjODIxNztzIG91dHNpZGUgb2YgdGhlIG1lbWJyYW5lPw==
Cgo=[Qq]
[q]The image below represents a substrate-level phosphorylation. Which numbered part of the image is the enzyme?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID E=[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcMeKAnSBpcyB0aGUgZW56eW1lLg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIEVuenltZXMgYXJlIGxhcmdlIHByb3RlaW5zLCB1c3VhbGx5IG11Y2ggbGFyZ2VyIHRoYW4gdGhlaXIgc3Vic3RyYXRlcy4gV2hhdCYjODIxNztzIHRoZSBiaWdnZXN0IHRoaW5nIGluIHRoaXMgZGlhZ3JhbT8=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]The image below represents a substrate-level phosphorylation. Which numbered part of the image is the source of the phosphate that will convert ADP to ATP?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq Ay[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcMuKAnSBpc8KgdGhlIG1vbGVjdWxlIHRoYXQgcHJvdmlkZXMgdGhlIHBob3NwaGF0ZSB1c2VkIHRvIHBob3NwaG9yeWxhdGUgQURQIHRvIEFUUC4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIExvb2sgZm9yIGEgcGhvc3BoYXRlLWNvbnRhaW5pbmcgbW9sZWN1bGUgdGhhdCYjODIxNztzIA==bm90IEFEUCBvciBBRFAu
Cg==[Qq]
[q]The image below represents a substrate-level phosphorylation. Which numbered part of the image is ADP?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq Az[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcM+KAnSBpcyBBRFAu[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuwqBBRFAgc3RhbmRzIGZvciBhZGVub3NpbmUgZGlwaG9zcGhhdGUuICYjODIyMDtEaSYjODIyMTsgbWVhbnMgJiM4MjIwO3R3by4mIzgyMjE7IEZpbmQgYSBtb2xlY3VsZSB3aXRoIHR3byBwaG9zcGhhdGUgZ3JvdXBzIChyZXByZXNlbnRlZCBieSAmIzgyMjA7cCYjODIyMTsgd2l0aGluIGEgY2lyY2xlKS4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]The image below represents a substrate-level phosphorylation. Which numbered part of the image is ATP?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq A1[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcNeKAnSBpcyBBVFAu[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuwqBBVFAgc3RhbmRzIGZvciBhZGVub3NpbmUgdHJpcGhvc3BoYXRlLiAmIzgyMjA7VHJpJiM4MjIxOyBtZWFucyAmIzgyMjA7dGhyZWUuJiM4MjIxOyBGaW5kIGEgbW9sZWN1bGUgd2l0aCB0aHJlZcKgcGhvc3BoYXRlIGdyb3VwcyAocmVwcmVzZW50ZWQgYnkgJiM4MjIwO3AmIzgyMjE7IHdpdGhpbiBhIGNpcmNsZSku
Cg==[Qq]
[x][restart]
[/qwiz]
4.2. Cellular Respiration Overview
[qwiz random = “true” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Cellular Respiration Overview Quiz 2, APBVP”]
[h]Cellular Respiration Overview Quiz 2
[i]
[q]Which phase is glycolysis?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]ID E=[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcMeKAnSBpcyBnbHljb2x5c2lz[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIEdseWNvbHlzaXMgbWVhbnMgJiM4MjIwO3NwbGl0dGluZyBzdWdhci4mIzgyMjE7IExvb2sgZm9yIGEgc3VnYXIsIGFuZCBsb29rIGZvciBhIHByb2Nlc3MgdGhhdCBzcGxpdHMgaXQgYXBhcnQu
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which phase is the link reaction?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq Ay[Qq]
[f]IFllcywg4oCcMuKAnSBpc8KgdGhlIGxpbmsgcmVhY3Rpb24u[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIFRoZSBsaW5rIHJlYWN0aW9uIGxpbmtzIGdseWNvbHlzaXMgKHdoaWNoIG1lYW5zICYjODIyMDtzcGxpdHRpbmcgc3VnYXImIzgyMjE7KSB3aXRoIHRoZSBLcmVicyBjeWNsZS4gV2hpY2ggbnVtYmVyIGluZGljYXRlcyBhIHByb2Nlc3MgdGhhdCBsaW5rcyBzb21ldGhpbmcgdGhhdCBzcGxpdHMgc3VnYXIgd2l0aCBzb21ldGhpbmcgdGhhdCBsb29rcyBjeWNsaWNhbD8=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which phase of cellular respiration is the electron transport chain?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq A0[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4gVGhlIGRlc2NlbmRpbmcgc3RhaXJ3YXkgb24gdGhlIGZhciByaWdodCB3aXRoIHRoZSBwcm9kdWN0aW9uIG9mIDI2IG9yIDI4IEFUUHMgaXMgdGhlIGVsZWN0cm9uIHRyYW5zcG9ydCBjaGFpbi4=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIFRoZSBlbGVjdHJvbiB0cmFuc3BvcnQgY2hhaW4gaW52b2x2ZXMgYSBzZXJpZXMgb2YgZW56eW1lcyB0aGF0IGFjY2VwdCBhbmQgaGFuZCBvZmYgZW5lcmdldGljIGVsZWN0cm9ucyBmcm9tIE5BREggYW5kIEZBREg=MiwgY3JlYXRpbmcgY29uZGl0aW9ucyBmb3IgZ2VuZXJhdGluZyBtb3JlIEFUUCB0aGFuIGFueSBvdGhlciBwYXJ0IG9mIGNlbGx1bGFyIHJlc3BpcmF0aW9uLiBXaGljaCBwaGFzZSBvZiBjZWxsdWxhciByZXNwaXJhdGlvbiBnZW5lcmF0ZXMgdGhlIG1vc3QgQVRQPw==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which phase of cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq Ax[Qq]
[f]IFllcy7CoEdseWNvbHlzaXMgb2NjdXJzIGluIHRoZSBjeXRvcGxhc20u[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIEl0IGludm9sdmVzIHNwbGl0dGluZyBnbHVjb3NlIGludG8gdHdvIG1vbGVjdWxlcyBvZiBweXJ1dmF0ZS4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which phase of cellular respiration occurs primarily along the inner mitochondrial membrane?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq A0[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4gVGhlIGVsZWN0cm9uIHRyYW5zcG9ydCBjaGFpbiwgc2hvd24gaW4gJiM4MjIwOzQsJiM4MjIxOyBoYXBwZW5zIGFsb25nIHRoZSBpbm5lciBtaXRvY2hvbmRyaWFsIG1lbWJyYW5lLg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuwqBUaGlzIHBoYXNlLCB3aGljaCBvY2N1cnMgYWxvbmcgdGhlIGlubmVyIG1pdG9jaG9uZHJpYWwgbWVtYnJhbmUsIGludm9sdmVzIGEgc2VyaWVzIG9mIGVuenltZXMgdGhhdCBhY2NlcHQgYW5kIGhhbmQgb2ZmIGVuZXJnZXRpYyBlbGVjdHJvbnMgZnJvbSBOQURIIGFuZCBGQURIMiwgY3JlYXRpbmcgY29uZGl0aW9ucyBmb3IgZ2VuZXJhdGluZyBtb3JlIEFUUCB0aGFuIGFueSBvdGhlciBwYXJ0IG9mIGNlbGx1bGFyIHJlc3BpcmF0aW9uLiBXaGljaCBwaGFzZSBvZiBjZWxsdWxhciByZXNwaXJhdGlvbiBnZW5lcmF0ZXMgdGhlIG1vc3QgQVRQPw==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Glycolysis occurs in which area of the cell?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq Az[Qq]
[f]IFllcy7CoEdseWNvbHlzaXMgb2NjdXJzIGluIHRoZSBjeXRvcGxhc20sIGF0IG51bWJlciAzLg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIFRoaXMgaXMgdGhlIG9uZSBwaGFzZSB0aGF0IG9jY3VycyBvdXRzaWRlIG9mIHRoZSBtaXRvY2hvbmRyaW9uLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Where does the Krebs cycle occur?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq A1[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4gVGhlIEtyZWJzIGN5Y2xlIG9jY3VycyBpbiB0aGUgbWl0b2Nob25kcmlhbCBtYXRyaXgsIG51bWJlciA1Lg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIEtyZWJzIG9jY3VycyBpbiB0aGUgY2VudHJhbCBmbHVpZCAoaG9tb2xvZ291cyB0byB0aGUgY3l0b3BsYXNtKSBvZiB0aGUgbWl0b2Nob25kcmlvbi4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Where is the electron transport chain found?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq A2[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4gVGhlIGVsZWN0cm9uIHRyYW5zcG9ydCBjaGFpbiBpcyBsb2NhdGVkwqBhbG9uZyB0aGUgaW5uZXIgbWVtYnJhbmUgb2YgdGhlIG1pdG9jaG9uZHJpb24=[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuwqBUaGUgZWxlY3Ryb24gdHJhbnNwb3J0IGNoYWluIGludm9sdmVzIG1lbWJyYW5lLWVtYmVkZGVkIGVuenltZXMuIFRoZXJlIGFyZSBtZW1icmFuZXMgc2hvd24gaW4gdGhpcyBkaWFncmFtIGF0IDIsIDYsIGFuZCA4LiBXaGljaCBvbmUgd291bGQgaGF2ZSB0aGUgZWxlY3Ryb24gdHJhbnNwb3J0IGNoYWluPw==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which of the molecules below can be made by substrate-level phosphorylation?
[c]TkFESA==[Qq]
[c]RkFESA==Mg==[Qq]
[c]QV RQ[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIE5BREggaXMgbWFkZSBieSBveGlkaXppbmcgZ2x1Y29zZSAob3Igb3RoZXIgZm9vZHMpLCB3aGljaCByZWR1Y2VzIE5BRA==Kw==IHRvIE5BREg=[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEZBREg=Mg==IGlzIG1hZGUgYnkgb3hpZGl6aW5nIGdsdWNvc2UgKG9yIG90aGVyIGZvb2RzKSwgd2hpY2ggcmVkdWNlcyBGQUTCoHRvIEZBREg=Mg==[Qq]
[f]WWVzISBBVFAgY2FuIGJlIG1hZGUgdGhyb3VnaCBzdWJzdHJhdGUtbGV2ZWwgcGhvc3Bob3J5bGF0aW9uLCB3aGljaCBpbnZvbHZlcyBlbnp5bWVzIHRyYW5zZmVycmluZyBhIHBob3NwaGF0ZSBmcm9tIHNvbWUgb3JnYW5pYyBzdWJzdHJhdGUgdG8gQURQLCBjcmVhdGluZyBBVFAu
Cg==[Qq]
[q]NADH is
[c]b3hpZGl6ZWQ=[Qq]
[c]cmVkdW NlZA==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIE5BREggaXMgdGhlIHJlZHVjZWQgZm9ybSBvZiB0aGlzIGVsZWN0cm9uIGNhcnJpZXIuwqBOQUQ=Kw==wqBpcyB0aGUgb3hpZGl6ZWQgZm9ybS4=[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBOQURIIGlzIHRoZSByZWR1Y2VkIGZvcm0gb2YgdGhpcyBlbGVjdHJvbiBjYXJyaWVyLsKgTkFEKw==wqBpcyB0aGUgb3hpZGl6ZWQgZm9ybS4=
Cg==[Qq]
[q]FADH2 is
[c]b3hpZGl6ZWQ=[Qq]
[c]cmVkdW NlZA==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uRkFESA==Mg==IGlzIHRoZSByZWR1Y2VkwqBmb3JtIG9mIHRoaXMgZWxlY3Ryb24gY2Fycmllci4gRkFEwqBpcyB0aGUgb3hpZGl6ZWTCoGZvcm0u[Qq]
[f]WWVzLkZBREg=Mg==IGlzIHRoZSByZWR1Y2VkwqBmb3JtIG9mIHRoaXMgZWxlY3Ryb24gY2Fycmllci4gRkFEwqBpcyB0aGUgb3hpZGl6ZWTCoGZvcm0u
Cg==[Qq][q]Foods like sugar (including glucose) are
[c]b3hpZGl6ZWQ=[Qq]
[c]cmVkdW NlZA==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uwqBGb29kcyBhcmUgaGlnaGx5IHJlZHVjZWQgc3Vic3RhbmNlcywgd2l0aCBsb3RzIG9mIGVuZXJnZXRpYyBlbGVjdHJvbnMgdGhhdCBjYW4gYmUgaGFydmVzdGVkIGZvciBlbmVyZ3kgZHVyaW5nIGNlbGx1bGFyIHJlc3BpcmF0aW9uLg==[Qq]
[f]WWVzLiBGb29kcyBhcmUgaGlnaGx5IHJlZHVjZWQgc3Vic3RhbmNlcywgd2l0aCBsb3RzIG9mIGVuZXJnZXRpYyBlbGVjdHJvbnMgdGhhdCBjYW4gYmUgaGFydmVzdGVkIGZvciBlbmVyZ3kgZHVyaW5nIGNlbGx1bGFyIHJlc3BpcmF0aW9uLg==
Cg==Cg==[Qq][q]When a cell needs to release a small amount of energy to do some work, it removes phosphate from ATP by breaking the bond at ____ and attaching the phosphate to something else.
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq BB[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4gV2hlbiBhIGNlbGwgbmVlZHMgdG8gcmVsZWFzZSBhIHNtYWxsIGFtb3VudCBvZiBlbmVyZ3ksIGl0IHdpbGwgYnJlYWsgb2ZmIHRoZSBsYXN0IHBob3NwaGF0ZSBvbiBBVFAgYW5kIGF0dGFjaCB0aGF0IHBob3NwaGF0ZSB0byBhbm90aGVyIG1vbGVjdWxlLg==[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEl0JiM4MjE3O3MgdGhlIGJvbmQgdGhhdCBob2xkcyB0aGUgdGhpcmQgcGhvc3BoYXRlIHRvIHRoZSBzZWNvbmQgdGhhdCBuZWVkcyB0byBiZSBicm9rZW4gKHNvIHRoYXQgdGhlIHBob3NwaGF0ZSBjYW4gYmUgYXR0YWNoZWQgdG8gc29tZXRoaW5nIGVsc2UsIHJlbGVhc2luZyBlbmVyZ3kpLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which best describes the process shown below?
[c]b3hpZGF0aW9u[Qq]
[c]cmVkdWN0aW9u[Qq]
[c]c3Vic3RyYXRlIGxldmVsIH Bob3NwaG9yeWxhdGlvbg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIE5vdGljZSB0aGUgdHJhbnNmZXIgb2YgYSBwaG9zcGhhdGUgZ3JvdXAgYnkgYW4gZW56eW1lIHRvIEFUUC4=[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuIE5vdGljZSB0aGUgdHJhbnNmZXIgb2YgYSBwaG9zcGhhdGUgZ3JvdXAgYnkgYW4gZW56eW1lIHRvIEFUUC4=[Qq]
[f]RXhjZWxsZW50LiBUaGlzIGRpYWdyYW0gZGVwaWN0cyBzdWJzdHJhdGUtbGV2ZWwgcGhvc3Bob3J5bGF0aW9uLg==
Cg==[Qq]
[q]Which phase of cellular respiration is the Krebs cycle?
[textentry single_char=”true”]
[c]wq Az[Qq]
[f]IFllcy7CoFRoZSBLcmVicyBjeWNsZSBpcyBzaG93biBhdCAmIzgyMjA7My4mIzgyMjE7[Qq]
[c]Kg==[Qq]
[f]Tm8uIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQuwqBUaGUgS3JlYnMgY3ljbGUgcHJvZHVjZXMgbW9yZSBOQURIIGFuZCBGQURIMg==IHRoYW4gYW55IG90aGVyIHBhcnQgb2YgY2VsbHVsYXIgcmVzcGlyYXRpb24uIFdoaWNoIHBoYXNlIGlzIHByb2R1Y2luZyB0aGUgbW9zdMKgTkFESCBhbmQgRkFESA==Mg==Pw==[Qq]
[x][restart]
[/qwiz]
What’s Next?
Please proceed to the next tutorial: Glycolysis, The Link Reaction, and the Krebs Cycle
