1. Watch this Video
2. Study this Summary
Carbohydrates
- Types:
- Monosaccharides (simple sugars like glucose) are the monomers (building blocks) of carbohydrates. The monosaccharide glucose is a product of photosynthesis, and is the starting point for cellular respiration.
- Disaccharides: Two linked monosaccharides (e.g., lactose, sucrose). Often used for energy transfer (lactose transfers energy between a mother and its babies; sucrose transfers energy between leaves and other parts of plants).
- Polysaccharides:
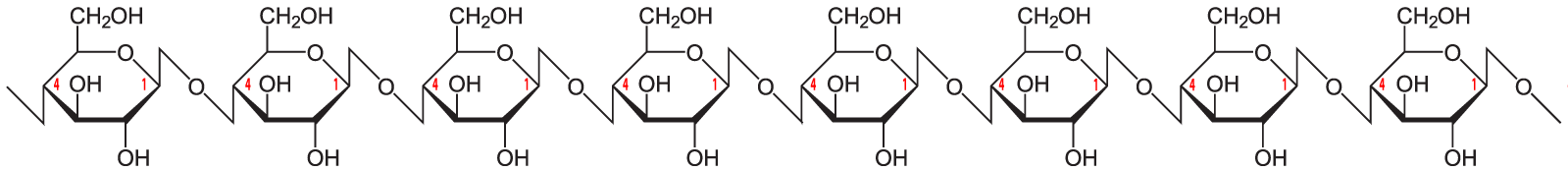
Cellulose: a polysaccharide - Three or more linked monosaccharides.
- Functions:
- Energy Storage: Starch (plants), glycogen (animals).
- Structural: Cellulose is the primary component of plant cell walls.
- Illustrative example: Cellulose digestion:
- Humans and most other animals lack the digestive enzymes to hydrolyze cellulose into the glucose monomers that make it up. As a result, cellulose can’t serve us as an energy source (but serves as an important source of fiber in the diet). Cellulose can be hydrolyzed into glucose by a group of mammals called ruminants (such as cows, deer, goats, etc). which have symbiotic relationships with bacteria that can break bonds in cellulose and release the glucose monomers. Among insects, termites can do the same (which is why they can digest wood).
- Illustrative example: Lactose Tolerance and Intolerance:
- Lactose is a disaccharide; the enzyme lactase breaks it into two monosaccharides, glucose and galactose.
- Most mammals produce lactase only during infancy.
- Mutations in some human populations allowed lactase persistence into adulthood, leading to lactose tolerance in specific regions (e.g., parts of Africa, Europe, and the Indian subcontinent). This opened a new food source to these populations. But worldwide, most adults are lactose intolerant.
- Lactose-intolerant individuals can use lactase supplements or lactose-free products.
Lipids
- Defining Features:
- Lipids are nonpolar or partially nonpolar, making them hydrophobic.
- Unlike carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids, lipids are not composed of repeating monomers.
- Types and Functions:
- Fats and Oils (Triglycerides):
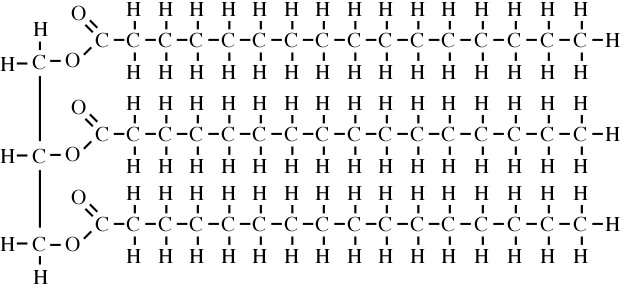
Fats are solid at room temperature. The fatty acid chains have no double bonds. - Function: Energy storage, insulation (as blubber in whales and other marine mammals), and buoyancy (also in marine mammals)
- Structure: fatty acids consist of a glycerol bound to three fatty acids.
- Fats are generally solid at room temperature, and are found more frequently in animals. Their fatty acids tend to be saturated fats (without double bonds in the fatty acid chain.
- Oils are generally liquid at room temperature, found more frequently in plants, and their fatty acids tend to be unsaturated (with one or more fatty acids in the fatty acid chain).
- Waxes: Used for waterproofing (as in the upper surfaces of leaves).
- Phospholipids: Key structural molecules in cell membranes.
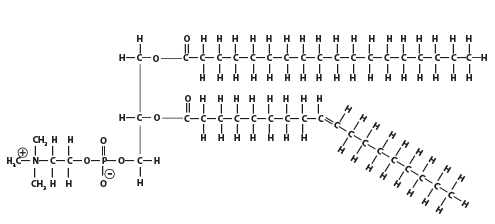
A phospholipid: note the polar head and nonpolar tail. - Structure: Phospholipids are composed of a hydrophilic (polar) head and two hydrophobic (nonpolar) tails. Connecting the head and tail is a glycerol molecule.
- In water, they form bilayers, with heads facing outward toward water and tails inward. This creates the structural framework of cell membranes.
- Steroids: Signaling molecules (e.g., hormones like estrogen and testosterone). Cholesterol plays a key role in cell membranes.
- Fats and Oils (Triglycerides):
3. Master these Flashcards
[qdeck qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Carbohydrates and Lipids Flashcards, APBVP”]
[h]Carbohydrates and Lipids
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1f7be4afe1110″ question_number=”17″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] What are the three types of carbohydrates?
[a] Carbohydrates include monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|6efa613b3696″ question_number=”18″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] Describe the basic structure and biological importance of monosaccharides.
[a] Monosaccharides (such as glucose or fructose) are simple sugars, composed of a single carbohydrate monomer. Monosaccharides are often energy sources, powering cellular respiration. Glucose is also the product of photosynthesis.
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|6e32253c9e96″ question_number=”19″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] Describe the basic structure and biological importance of disaccharides.
[a] Disaccharides (such as lactose and sucrose) are composed of two monosaccharides. Disaccharides are often used for energy transfer. Lactose (milk sugar) transfers energy from a mammalian mother to her offspring. Sucrose (shown below) is composed of one glucose (a) bonded to one fructose (b). Sucrose is used to transfer energy from the leaves of a plant to other, non-photosynthetic parts.
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|6d36b0386e96″ question_number=”20″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] Describe the basic structure and biological importance of polysaccharides.
[a] Polysaccharides are carbohydrate polymers, composed of 3 or more monosaccharides linked together. Starch and glycogen are polymers of glucose and are used for energy storage (starch in plants, glycogen in animals). Cellulose (also a polymer of glucose) is used to build the cell walls of plants.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1f681a4acf110″ question_number=”21″ topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] Starch and cellulose are both polysaccharides, yet their biological functions are different. Describe the function of each, and explain their differences.
[a] Both starch and cellulose are polymers of glucose. Starch is used by plants to store energy; cellulose is used to build cell walls. Starch can be used for energy storage because the bond that connects the glucose monomers in starch is easily hydrolyzed by enzymes in many species, including humans. Cellulose, by contrast, can’t be digested by humans. That’s because the bonds between the glucose monomers in cellulose have a configuration that few animal enzymes can hydrolyze. As a result, cellulose, when ingested, serves as a source of fiber, but not energy.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1f542aa4fed10″ question_number=”23″ topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] Describe the basic chemistry, overall structure, and biological importance of lipids.
[a] Lipids are molecules that are either non-polar or have large nonpolar regions. Many lipids are built of one or more fatty acids (shown below), which are hydrocarbon chains that end in a carboxyl group. Lipids are used for energy storage, waterproofing, as essential components of cell membranes, and as building blocks for steroid hormones.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1f4a2031b7910″ question_number=”24″ topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] List the four key types of lipids. Briefly describe the function of each.
[a] Lipids include
- triglycerides (fats and oils), which are used for energy storage and insulation;
- waxes, which are used for waterproofing;
- phospholipids, which are the key structural components of cell membranes;
- and steroids, which are signaling molecules (steroid hormones).
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|21b1bfd2095da6″ question_number=”25″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] Compare and contrast fats and oils.
[a] Both fats and oils are triglycerides, with three fatty acids bonded to a glycerol molecule (a 3-carbon alcohol). In fats, the fatty acids tend to be unsaturated, and the resulting fat molecule is a solid at room temperature. In oils, one or more of the fatty acids is unsaturated, and the resulting oil molecule is liquid at room temperature.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1f3427017fd10″ question_number=”27″ topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] Describe the structure of phospholipids.
[a] The central molecule in a phospholipid is the 3-carbon alcohol glycerol (2). Bonded to the glycerol on one side are two fatty acids, forming the hydrophobic tail (3). On the other side of the glycerol is the hydrophilic head, which contains a negatively charged phosphate group. As a result, phospholipids have a polar, hydrophilic “head,” and a non-polar, hydrophobic “tail.”
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1f29f74d7a510″ question_number=”28″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] Explain the relationship between the structure of a phospholipid and the role that these molecules play in cell membranes.
[a] When phospholipids are mixed with water, the hydrophilic heads face out (interacting with water molecules), while the tails face inward, forming a water-free zone. In addition, the tails are attracted to one another by very weak intermolecular forces (called London Dispersion forces, or hydrophobic bonds). This interaction forms the basic structure of membranes, the phospholipid bilayer.
[q json=”true” yy=”4″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|1f1fc79974d10″ question_number=”29″ topic=”1.4.Carbohydrates_and_Lipids”] Describe the structure and function of steroids and waxes.
[a] Steroids consist of four or five fused carbon rings, often with hydrocarbons attached. They’re the starting point for steroid hormones (important signaling molecules). Cholesterol is a steroid that plays a stabilizing role in cell membranes.
Waxes consist of two or more hydrocarbon chains that are bonded together. They play an important waterproofing role, especially in leaves, where waxes coat the surface of leaves, reducing water loss.
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|added1″ question_number=”1″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.2.Lactose_Tolerance”] What is lactose, and how is it broken down in the body?
[a] Lactose is a disaccharide composed of two monosaccharides, glucose and galactose. The enzyme lactase breaks lactose into these monosaccharides, enabling their absorption in the small intestine.
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|added2″ question_number=”2″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.2.Lactose_Tolerance”] Why do most mammals stop producing lactase after infancy?
[a] Most mammals stop producing lactase after infancy because they no longer consume milk. Evolutionarily, it is energy-efficient to stop producing an enzyme for a food source that is no longer consumed.
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|added3″ question_number=”3″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.2.Lactose_Tolerance”] How did lactase persistence evolve in certain human populations?
[a] Lactase persistence evolved in human populations with a history of herding goats, sheep, cows, camels, etc. These populations were located in Africa, Europe, and the Indian subcontinent. Mutations allowed these populations to continue producing lactase into adulthood, enabling them to digest milk and exploit dairy products as a food source.
[q json=”true” dataset_id=”AP_Bio_Flashcards_2022|added4″ question_number=”4″ unit=”1.Chemistry_of_Life” topic=”1.2.Lactose_Tolerance”] How can lactose-intolerant individuals manage their condition?
[a] Lactose-intolerant individuals can manage their condition by using lactase supplements or consuming lactose-free products that have already been processed to remove lactose.
[x]
[restart]
[/qdeck]
4. Tackle these Quizzes
4.1. Carbohydrates
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Carbohydrates, APBVP”]
[h]Carbohydrates
[i]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem2_Monosaccharides|6e29ecb2bae76″ question_number=”1″] Monosaccharides are the monomers of [hangman]
[c]IGNhcmJvaHlkcmF0ZXM=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem2_Monosaccharides|6e01532363276″ question_number=”9″] This sugar is the most common carbohydrate monomer. It’s the starting point for cellular respiration. Inability to control this sugar is associated with diabetes.
This sugar is called [hangman]
[c]IGdsdWNvc2U=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem3_disaccharides|121104b564c12a” question_number=”2″]Disaccharides often have the function of energy [hangman].
[c]IHRyYW5zZmVy[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem3_disaccharides|1210c1300bed2a” question_number=”3″] The disaccharide in milk is [hangman].
[c]bGFjdG9zZQ==[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem3_disaccharides|12107b56a7352a” question_number=”4″] The disaccharide in a sugar cube is [hangman].
[c]c3Vjcm9zZQ==[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem3_disaccharides|121029d907092a” question_number=”5″] Monosaccharides get combined into disaccharides through [hangman] synthesis.
[c]ZGVoeWRyYXRpb24=[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem3_disaccharides|120fe3ffa2512a” question_number=”6″] Bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea associated with drinking milk are symptoms of possible [hangman] intolerance.
[c]bGFjdG9zZQ==[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem3_disaccharides|120f972a19ed2a” question_number=”7″] Most mammals can only produce [hangman]-digesting enzymes until they are weaned.
[c]bGFjdG9zZQ==
Cg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem3_disaccharides|120f171b8bf12a” question_number=”8″]Digestion of a disaccharide results in two [hangman].
[c]bW9ub3NhY2NoYXJpZGVz[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem4_carbohydrates_cumulative|7c4c67623fb15″ question_number=”3″] Carbohydrates like cellulose and starch are classified as[hangman]
[c]IHBvbHlzYWNjaGFyaWRlcw==[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[q json=”true” multiple_choice=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem4_carbohydrates_cumulative|7c45b5c010315″ question_number=”4″] Of the following polysaccharides, the one that humans can’t digest for food energy is
[c]IGdseWNvZ2Vu[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBHbHljb2dlbiBpcyBzb21ldGltZXMgY2FsbGVkICYjODIyMDthbmltYWwgc3RhcmNoLiYjODIyMTsgSXQgd291bGQgYmUgdW51c3VhbCB0byBlYXQgYSBsb3Qgb2YgaXQsIGJ1dCBpZiB5b3UgaW5nZXN0ZWQgaXQsIHlvdSBjb3VsZCBicmVhayBpdHMgYm9uZHMgYXBhcnQgdG8gcHJvZHVjZSBnbHVjb3NlLiBUaGUgcG9seXNhY2NoYXJpZGUgeW91JiM4MjE3O3JlIGxvb2tpbmcgZm9yIGlzIHRoZSBvbmUgdGhhdCBtYWtlcyB1cCBwbGFudCBjZWxsIHdhbGxzLg==[Qq]
[c]IGNlbGx1 bG9zZQ==[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3QuIFRoZSBib25kcyBob2xkaW5nIGdsdWNvc2UgbW9ub21lcnMgdG9nZXRoZXIgaW4gY2VsbHVsb3NlIGNhbiYjODIxNzt0IGJlIGJyb2tlbiBkb3duIGJ5IHRoZSBodW1hbiBkaWdlc3RpdmUgc3lzdGVtLiBBcyBhIHJlc3VsdCwgY2VsbHVsb3NlIGlzIG5vdCBhIHNvdXJjZSBvZiBmb29kIGVuZXJneS4=[Qq]
[c]IHN0YXJjaA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBTdGFyY2ggaXMgYSBwb2x5c2FjY2hhcmlkZSB0aGF0IGh1bWFucyBjYW4gZWFzaWx5IGJyZWFrIGRvd24gaW50byBnbHVjb3NlIG1vbm9tZXJzIHRoYXQgY2FuIHNlcnZlIGFzIGFuIGVuZXJneSBzb3VyY2UuIFRoZSBwb2x5c2FjY2hhcmlkZSB5b3UmIzgyMTc7cmUgbG9va2luZyBmb3IgaXMgdGhlIG9uZSB0aGF0IG1ha2VzIHVwIHBsYW50IGNlbGwgd2FsbHMu[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem4_carbohydrates_cumulative|7c282b6933715″ question_number=”9″] When you eat foods like spaghetti, your body will take the starch in the spaghetti and, in several steps, convert the spaghetti into its monomer, which is [hangman].
[c]IGdsdWNvc2U=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q json=”true” multiple_choice=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem4_carbohydrates_cumulative|7c16ff9181f15″ question_number=”12″] If your doctor tells you to get more fiber in your diet, then she or he is telling you to ingest which kind of carbohydrate?
[c]IGdseWNvZ2Vu[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBHbHljb2dlbiBpcyBhIG1vbGVjdWxlIHRoYXQmIzgyMTc7cyB2ZXJ5IHNpbWlsYXIgdG8gc3RhcmNoLiBJdCBzdG9yZXMgZW5lcmd5LCBidXQgaXQmIzgyMTc7cyBub3QgZmliZXIuIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQ6IHRoZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBsb3Qgb2YgZmliZXIgaW4gcGxhbnQgY2VsbCB3YWxscy4gV2hhdCBtb2xlY3VsZSBtYWtlcyB1cCB0aG9zZSBjZWxsIHdhbGxzPw==[Qq]
[c]IGNlbGx1 bG9zZQ==[Qq]
[f]IFllcy4gQ2VsbHVsb3NlIGlzIHRoZSBtb2xlY3VsZSB0aGF0IG1ha2VzIHVwIHBsYW50IGZpYmVyLg==[Qq]
[c]IFN0YXJjaA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBTdGFyY2ggaXMgYSBwb2x5c2FjY2hhcmlkZSB0aGF0IHN0b3JlcyBlbmVyZ3ksIGJ1dCBpdCYjODIxNztzIG5vdCBmaWJlci4gSGVyZSYjODIxNztzIGEgaGludDogdGhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGxvdCBvZiBmaWJlciBpbiBwbGFudCBjZWxsIHdhbGxzLiBXaGF0IG1vbGVjdWxlIG1ha2VzIHVwIHRob3NlIGNlbGwgd2FsbHM/[Qq]
[c]IExhY3Rvc2U=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBMYWN0b3NlIGlzIGEgZGlzYWNjaGFyaWRlIGFuZCBub3QgYSBzb3VyY2Ugb2YgZmliZXIuIEhlcmUmIzgyMTc7cyBhIGhpbnQ6IHRoZXJlJiM4MjE3O3MgYSBsb3Qgb2YgZmliZXIgaW4gcGxhbnQgY2VsbCB3YWxscy4gV2hhdCBtb2xlY3VsZSBtYWtlcyB1cCB0aG9zZSBjZWxsIHdhbGxzPw==
Cg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem4_carbohydrates_cumulative|7c0439f1a3b15″ question_number=”14″] If the molecule below is starch, then the monomers making up this molecular are [hangman].
[c]IGdsdWNvc2U=[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[x][restart]
[/qwiz]
4.2. Lipids
[qwiz qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Lipids, APBVP”]
[h]Lipids
[i]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem5_fats_and_oils|7beb7cf34d315″ question_number=”1″] Lipids are mostly [hangman]. That means that, for the most part, they won’t dissolve in water.
[c]IGh5ZHJvcGhvYmlj[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh
Cg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem5_fats_and_oils|7be61a97cdf15″ question_number=”2″] Review question: The kind of bond that lipids won’t form with water is a [hangman] bond.
[c]IGh5ZHJvZ2Vu[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem5_fats_and_oils|7bd046a854715″ question_number=”6″] One of the key functions of fats and oils is their ability to store lots of[hangman].
[c]IGVuZXJneQ==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=
Cg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem5_fats_and_oils|7bc581f155f15″ question_number=”8″] In addition to energy storage, the fatty blubber found in marine mammals provides them with a layer of [hangman] to protect them from heat loss.
[c]IGluc3VsYXRpb24=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q json=”true” multiple_choice=”true” xx=”3″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem6_lipids_cumulative|8ce25c964a33b” question_number=”1″] The molecule shown below is a
[c]IGZhdHR5IGFjaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBGYXR0eSBhY2lkcyBoYXZlIGEgbG9uZyBoeWRyb2NhcmJvbiB0YWlsLCBhdHRhY2hlZCB0byBhIGNhcmJveHlsIGdyb3VwLiBOb3RlIHRoZSBmb3VyIGZ1c2VkIGNhcmJvbiByaW5ncy4=
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IHRyaWdseWNlcmlkZQ==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUcmlnbHljZXJpZGVzIGhhdmUgdGhyZWUgZmF0dHkgYWNpZHMgYXR0YWNoZWQgdG8gb25lIGdseWNlcm9sLg==[Qq]
[c]IHdheA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBXYXhlcyB1c3VhbGx5IGNvbnNpc3Qgb2YgdHdvIGxvbmcgaHlkcm9jYXJib24gY2hhaW5z
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IHN0ZX JvaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gVGhpcyBtb2xlY3VsZSBpcyBhIHN0ZXJvaWQgKHNwZWNpZmljYWxseSwgaXQmIzgyMTc7cyB0aGUgaG9ybW9uZSBlc3Ryb2dlbik=[Qq]
[c]IHBob3NwaG9saXBpZA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBQaG9zcGhvbGlwaWRzIGNvbnNpc3Qgb2YgdHdvIG5vbi1wb2xhciBmYXR0eSBhY2lkIGNoYWlucywgYXR0YWNoZWQgdG8gZ2x5Y2Vyb2wsIHdoaWNoIGlzIGF0dGFjaGVkIHRvIGEgcG9sYXIgJiM4MjIwO2hlYWQmIzgyMjE7IGNvbnNpc3Rpbmcgb2YgYSBwaG9zcGhhdGUgZ3JvdXA=
Cg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” multiple_choice=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem6_lipids_cumulative|8cd4f951eb33b” question_number=”4″] The molecule shown below is a
[c]IGZhdHR5IGFjaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUaGlzIG1vbGVjdWxlIGNvbnRhaW5zIGZhdHR5IGFjaWRzICh0aHJlZSBvZiB0aGVtLCBpbiBmYWN0KSwgYnV0IGl0JiM4MjE3O3Mgbm90IGp1c3QgYSBmYXR0eSBhY2lkLiBBIHNpbmdsZSBmYXR0eSBhY2lkIGlzIHNob3duIGJlbG93
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IGZhdCAodHJpZ2 x5Y2VyaWRlKQ==[Qq]
[f]IE5pY2Ugam9iLiBUcmlnbHljZXJpZGVzIGhhdmUgdGhyZWUgZmF0dHkgYWNpZHMgYXR0YWNoZWQgdG8gb25lIGdseWNlcm9sLg==[Qq]
[c]IHdheA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBXYXhlcyBjb25zaXN0IG9mIHR3byBsb25nIGh5ZHJvY2FyYm9uIGNoYWlucywgYXQgbGVhc3Qgb25lIG9mIHdoaWNoIGlzIGEgZmF0dHkgYWNpZC4=
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IHN0ZXJvaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBTdGVyb2lkcyBjb25zaXN0IG9mIGZvdXIgZnVzZWQgY2FyYm9uIHJpbmdzLCBhcyBzaG93biBiZWxvdy4=
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IHBob3NwaG9saXBpZA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBQaG9zcGhvbGlwaWRzIGNvbnNpc3Qgb2YgdHdvIG5vbi1wb2xhciBmYXR0eSBhY2lkIGNoYWlucywgYXR0YWNoZWQgdG8gZ2x5Y2Vyb2wsIHdoaWNoIGlzIGF0dGFjaGVkIHRvIGEgcG9sYXIgJiM4MjIwO2hlYWQmIzgyMjE7IGNvbnNpc3Rpbmcgb2YgYSBwaG9zcGhhdGUgZ3JvdXAu
Cg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” multiple_choice=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem6_lipids_cumulative|8cd09bbb9fb3b” question_number=”5″] The molecule shown below is a
[c]IGZhdHR5IGFjaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUaGlzIG1vbGVjdWxlIGNvbnRhaW5zIGZhdHR5IGFjaWRzICh0d28gb2YgdGhlbSwgaW4gZmFjdCksIGJ1dCBpdCYjODIxNztzIG5vdCBqdXN0IGEgZmF0dHkgYWNpZC4gQSBzaW5nbGUgZmF0dHkgYWNpZCBpcyBzaG93biBiZWxvdy4=
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IHRyaWdseWNlcmlkZQ==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUcmlnbHljZXJpZGVzIGhhdmUgdGhyZWUgZmF0dHkgYWNpZHMgYXR0YWNoZWQgdG8gb25lIGdseWNlcm9sLg==[Qq]
[c]IHdheA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBXYXhlcyBjb25zaXN0IG9mIHR3byBsb25nIGh5ZHJvY2FyYm9uIGNoYWlucywgYXQgbGVhc3Qgb25lIG9mIHdoaWNoIGlzIGEgZmF0dHkgYWNpZC4=
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IHN0ZXJvaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBTdGVyb2lkcyBjb25zaXN0IG9mIGZvdXIgZnVzZWQgY2FyYm9uIHJpbmdzLCBhcyBzaG93biBiZWxvdy4=
Cg==[Qq]
[c]IHBob3NwaG 9saXBpZA==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gUGhvc3Bob2xpcGlkcyBjb25zaXN0IG9mIHR3byBub24tcG9sYXIgZmF0dHkgYWNpZCBjaGFpbnMsIGF0dGFjaGVkIHRvIGdseWNlcm9sLCB3aGljaCBpcyBhdHRhY2hlZCB0byBhIHBvbGFyICYjODIyMDtoZWFkJiM4MjIxOyBjb25zaXN0aW5nIG9mIGEgcGhvc3BoYXRlIGdyb3VwLg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” multiple_choice=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem6_lipids_cumulative|8ccc63661273b” question_number=”6″] A molecule that’s the key building block of cell membranes.
[c]IHN0ZXJvaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBXaGlsZSBjaG9sZXN0ZXJvbCBpcyBhIHN0ZXJvaWQgdGhhdCYjODIxNztzIGEgcGFydCBvZiBjZWxsIG1lbWJyYW5lcywgaXQmIzgyMTc7cyBub3QgdGhlIG1haW4gY29tcG9uZW50LiBZb3UmIzgyMTc7cmUgbG9va2luZyBmb3Igc29tZXRoaW5nIHRoYXQgb3JnYW5pemVzIGl0c2VsZiBpbnRvIGEgYmlsYXllci4=[Qq]
[c]IHRyaWdseWNlcmlkZQ==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUcmlnbHljZXJpZGVzIGFyZSB1c2VkIGZvciBlbmVyZ3kgc3RvcmFnZSwgaW5zdWxhdGlvbiwgYW5kIGJ1b3lhbmN5LiBZb3UmIzgyMTc7cmUgbG9va2luZyBmb3Igc29tZXRoaW5nIHRoYXQgb3JnYW5pemVzIGl0c2VsZiBpbnRvIGEgYmlsYXllci4=[Qq]
[c]IHBob3NwaG 9saXBpZA==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gUGhvc3Bob2xpcGlkcyBhcmUgdGhlIGtleSBidWlsZGluZyBibG9ja3Mgb2YgY2VsbCBtZW1icmFuZXMu[Qq]
[c]IHdheA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBXYXhlcyBhcmUgdXNlZCBmb3Igd2F0ZXJwcm9vZmluZy4gWW91JiM4MjE3O3JlIGxvb2tpbmcgZm9yIGEgbW9sZWN1bGUgdGhhdCBvcmdhbml6ZXMgaXRzZWxmIGludG8gYSBiaWxheWVyLg==[Qq]
[q json=”true” multiple_choice=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem6_lipids_cumulative|8cc805cfc6f3b” question_number=”7″] A molecule that’s used for energy storage, insulation, and buoyancy.
[c]IHN0ZXJvaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBTdGVyb2lkcyBpbmNsdWRlIGhvcm1vbmVzIGxpa2UgdGVzdG9zdGVyb25lIGFuZCBlc3Ryb2dlbiwgYW5kIGFsc28gbW9sZWN1bGVzIGxpa2UgY2hvbGVzdGVyb2wsIGEga2V5IGNvbXBvbmVudCBvZiBjZWxsIG1lbWJyYW5lcy4=[Qq]
[c]IHRyaWdseW NlcmlkZQ==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCEgVHJpZ2x5Y2VyaWRlcyBpbmNsdWRlIGZhdHMgYW5kIG9pbHMuIFRoZXkmIzgyMTc7cmUgdXNlZCBmb3IgZW5lcmd5IHN0b3JhZ2UsIGluc3VsYXRpb24sIGFuZCBidW95YW5jeS4=[Qq]
[c]IHBob3NwaG9saXBpZA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBQaG9zcGhvbGlwaWRzIGFyZSB0aGUga2V5IGJ1aWxkaW5nIGJsb2NrcyBvZiBjZWxsIG1lbWJyYW5lcy4=[Qq]
[c]IHdheA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBXYXhlcyBhcmUgdXNlZCBmb3Igd2F0ZXJwcm9vZmluZy4gWW91JiM4MjE3O3JlIGxvb2tpbmcgZm9yIHRoZSB0eXBlIG9mIG1vbGVjdWxlIHRoYXQgbWFrZXMgdXAgZmF0cyBhbmQgb2lscy4=[Qq]
[q json=”true” multiple_choice=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem6_lipids_cumulative|8cc35db7fef3b” question_number=”8″] The type of lipid that forms certain hormones, as well as the membrane component cholesterol.
[c]IHN0ZX JvaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IEF3ZXNvbWUhIFN0ZXJvaWRzIGluY2x1ZGUgaG9ybW9uZXMgbGlrZSB0ZXN0b3N0ZXJvbmUgYW5kIGVzdHJvZ2VuLCBhbmQgYWxzbyBtb2xlY3VsZXMgbGlrZSBjaG9sZXN0ZXJvbCwgYSBrZXkgY29tcG9uZW50IG9mIGNlbGwgbWVtYnJhbmVzLg==[Qq]
[c]IHRyaWdseWNlcmlkZQ==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUcmlnbHljZXJpZGVzIGluY2x1ZGUgZmF0cyBhbmQgb2lscy4gVGhleSYjODIxNztyZSB1c2VkIGZvciBlbmVyZ3kgc3RvcmFnZSwgaW5zdWxhdGlvbiwgYW5kIGJ1b3lhbmN5Lg==[Qq]
[c]IHBob3NwaG9saXBpZA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBQaG9zcGhvbGlwaWRzIGFyZSB0aGUga2V5IGJ1aWxkaW5nIGJsb2NrcyBvZiBjZWxsIG1lbWJyYW5lcy4=[Qq]
[c]IHdheA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBXYXhlcyBhcmUgdXNlZCBmb3Igd2F0ZXJwcm9vZmluZy4=[Qq]
[q json=”true” multiple_choice=”true” xx=”2″ dataset_id=”SMV_biochem6_lipids_cumulative|8cbc619452f3b” question_number=”9″] A molecule used for waterproofing.
[c]IHN0ZXJvaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBTdGVyb2lkcyBpbmNsdWRlIGhvcm1vbmVzIGxpa2UgdGVzdG9zdGVyb25lIGFuZCBlc3Ryb2dlbiwgYW5kIGFsc28gbW9sZWN1bGVzIGxpa2UgY2hvbGVzdGVyb2wsIGEga2V5IGNvbXBvbmVudCBvZiBjZWxsIG1lbWJyYW5lcy4=[Qq]
[c]IHRyaWdseWNlcmlkZQ==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBUcmlnbHljZXJpZGVzIGluY2x1ZGUgZmF0cyBhbmQgb2lscy4gVGhleSYjODIxNztyZSB1c2VkIGZvciBlbmVyZ3kgc3RvcmFnZSwgaW5zdWxhdGlvbiwgYW5kIGJ1b3lhbmN5Lg==[Qq]
[c]IHBob3NwaG9saXBpZA==[Qq]
[f]IE5vLiBQaG9zcGhvbGlwaWRzIGFyZSB0aGUga2V5IGJ1aWxkaW5nIGJsb2NrcyBvZiBjZWxsIG1lbWJyYW5lcy4=[Qq]
[c]IHdh eA==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudC4gV2F4ZXMgYXJlIHVzZWQgZm9yIHdhdGVycHJvb2Zpbmcu[Qq]
[/qwiz]
What’s next?
Please proceed to this next tutorial: Proteins
