1. We’re all built from the same stuff: the four families of biological molecules
Think of the five most different living things that you can imagine.
I think of the California redwoods, the Archaea (a type of prokaryote) that live in the hot springs of Yellowstone National Park, bread mold, horseshoe crabs, and Orcas (also known as killer whales). But these organisms, despite their different forms, sizes, and ecological niches, are built from the same four types of molecules. Ignoring the water which makes up most of the mass of any organism, they’re each composed of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
You can see these biomolecules clearly identified in food labels.
Here’s the label for a bag of potato chips.
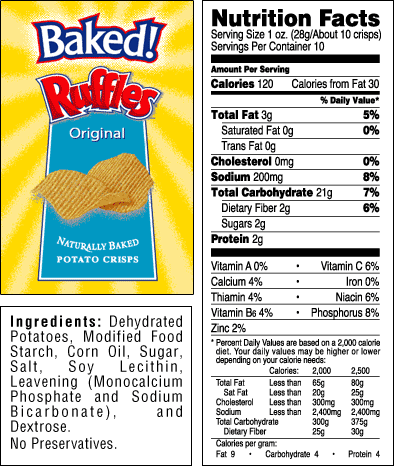
And here are chicken breasts.

To start to get to know these biomolecule families, study the descriptions below.
Carbohydrates include
- sugars,
- starches, and
- plant fiber (also known as cellulose).
Their monomers are simple sugars or monosaccharides.
Lipids include
- fats,
- oils,
- waxes,
- cholesterol, and
- steroid hormones like estrogen and testosterone
As we’ll see, lipids don’t fit into the polymer/monomer paradigm. But an important lipid building block to know is fatty acids.
Proteins include
- muscle tissue (meat);
- structural proteins that make up skin, hair, and fingernails;
- enzymes (which catalyze and control the chemical reactions in living things), and
- antibodies (immune system molecules that fight infectious organisms such as bacteria and viruses).
The monomers of proteins are amino acids.
Nucleic Acids include
- DNA: the molecule that makes up genes;
- RNA: a molecule used to direct cellular activities; and
- ATP: the molecule used by cells to meet their moment-to-moment energy needs.
The monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides.
Now, watch the video below, which will teach you more about each biomolecule family.
2. Video: The Four Biomolecule Families
3. Quiz: The Four Families of Biomolecules
[qwiz style=”width: 650px !important; min-height: 400px !important;” qrecord_id=”sciencemusicvideosMeister1961-Four Families of Biomolecules Overview (2.0)”]
[h] Quiz: The Four Families of Biomolecules
[i]
The quiz that follows includes a concept map and fill-in-the-blanks questions.
If you don’t get the answer right the first time, you get another try (so don’t stress about getting questions wrong: everybody learns at their own pace).
Note that answers might repeat
[q labels = “top”]
[l]fatty acid
[f*] Correct!
[fx] No. Please try again.
[l]lean meat
[f*] Excellent!
[fx] No. Please try again.
[l]lipids
[f*] Great!
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[l]monosaccharide
[f*] Good!
[fx] No. Please try again.
[l]proteins
[f*] Great!
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[l]nucleic acids
[f*] Correct!
[fx] No. Please try again.
[l]nucleotide
[f*] Great!
[fx] No. Please try again.
[l]starch
[f*] Correct!
[fx] No, that’s not correct. Please try again.
[q] In a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, both the bread and the jelly would be classified as [hangman].
[c]IGNhcmJvaHlkcmF0ZXM=[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] Fats, oils, waxes, and steroids are members of the [hangman] family.
[c]IGxpcGlk[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q] Foods like chicken, beef, and egg white are all members of the [hangman] biomolecule family.
[c]IHByb3RlaW4=[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q] The molecules of heredity, DNA and RNA, are [hangman] [hangman].
[c]IG51Y2xlaWM=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[c]IGFjaWRz[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q] Biomolecules are often composed of smaller building blocks, which are also known as [hangman].
[c]IG1vbm9tZXJz[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q] The monomers of carbohydrates are [hangman].
[c]IG1vbm9zYWNjaGFyaWRlcw==[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[q] Another term for “monosaccharide” is [hangman] sugar.
[c]IHNpbXBsZQ==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q] Sucrose, also known as table sugar, is formed by linking together two monosaccharides. That makes it a [hangman].
[c]IGRpc2FjY2hhcmlkZQ==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q] Both monosaccharides like glucose and disaccharides like sucrose are [hangman].
[c]IHN1Z2Fycw==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] The fondness for sugar shared by many animals (including humans) evolved because sugars are a quick source of [hangman].
[c]IGVuZXJneQ==[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q] The polysaccharide found in bread, pasta, and rice is called [hangman].
[c]IHN0YXJjaA==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] The polysaccharide that makes up plant fiber is called [hangman].
[c]IGNlbGx1bG9zZQ==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q] Cellulose makes up the cell [hangman] of plants.
[c]IHdhbGw=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q] Wood and cotton are both made of a polysaccharide called [hangman]
[c]IGNlbGx1bG9zZQ==[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[q] One thing that the lipids have in common is that they are, for the most part, [hangman], which is why they generally won’t dissolve in [hangman].
[c]IG5vbnBvbGFy[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[c]IHdhdGVy[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] The molecule below is a [hangman] [hangman], and it’s an important building block of [hangman].
[c]IGZhdHR5[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[c]IGFjaWQ=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[c]IGxpcGlkcw==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q] Fats and oils have more [hangman]/gram than any other type of food.
[c]IGVuZXJneQ==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] Marine mammals like whales use fat for [hangman].
[c]IGluc3VsYXRpb24=[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q] The molecule used for waterproofing, found on the upper and lower surface of leaves (see number 1 below), is [hangman].
[c]IHdheA==[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[q] The molecule shown below is a [hangman]. These molecules make up the basic structure of the cell [hangman].
[c]IHBob3NwaG9saXBpZA==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[c]IG1lbWJyYW5l[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[q] Both testosterone and estrogen are hormones that belong to a class of lipids called [hangman].
[c]IHN0ZXJvaWRz[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] The protein-based tissue that makes it possible for you to move (and which is what you eat when you eat chicken or beef) is [hangman]
[c]IG11c2NsZQ==[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] Antibodies and enzymes are both [hangman]
[c]IHByb3RlaW5z[Qq]
[f]IENvcnJlY3Qh[Qq]
[q] The monomers of proteins are [hangman] [hangman], one of which is shown below.
[c]IGFtaW5v[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[c]IGFjaWRz[Qq]
[f]IEdvb2Qh[Qq]
[q] The monomers of nucleic acids are [hangman], one of which is shown below.
[c]IG51Y2xlb3RpZGVz[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are the molecules of [hangman].
[c]IGhlcmVkaXR5[Qq]
[f]IEdyZWF0IQ==[Qq]
[q] Life’s key molecule for storing energy for powering work at the cellular level is a nucleotide called [hangman].
[c]IEFUUA==[Qq]
[f]IEV4Y2VsbGVudCE=[Qq]
[/qwiz]
What’s next?
- Continue to AP Bio Topic 1.4, Carbohydrates, the next tutorial in AP Bio Unit 1.
